Roles of PANoptosis and related genes in acute liver failure: neoteric insight from bioinformatics analysis and animal experiment verification
- PMID: 40274384
- PMCID: PMC12021540
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2300678
Roles of PANoptosis and related genes in acute liver failure: neoteric insight from bioinformatics analysis and animal experiment verification
Abstract
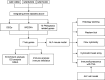
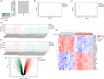
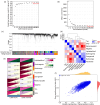
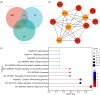
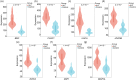
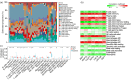
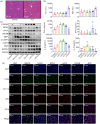
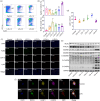
BACKGROUND: PANoptosis has the features of pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis. Numerous studies have confirmed the diverse roles of various types of cell death in acute liver failure (ALF), but limited attention has been given to the crosstalk among them. In this study, we aimed to explore the role of PANoptosis in ALF and uncover new targets for its prevention or treatment. METHODS: Three ALF-related datasets (GSE14668, GSE62029, and GSE74000) were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Hub genes were identified through intersecting DEGs, genes obtained from weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA), and genes related to PANoptosis. Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), protein‒protein interaction (PPI) analyses and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) were performed to determine functional roles. Verification was performed using an ALF mouse model. RESULTS: Our results showed that expression of seven hub genes (B-cell lymphoma-2-modifying factor (BMF), B-cell lymphoma-2-interacting protein 3-like (BNIP3L), Caspase-1 (CASP1), receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (RIPK3), uveal autoantigen with coiled-coil domains and ankyrin repeats protein (UACA), uncoordinated-5 homolog B receptor (UNC5B), and Z-DNA-binding protein 1 (ZBP1)) was up-regulated in liver samples of patients. However, in the ALF mouse model, the expression of BNIP3L, RIPK3, phosphorylated RIPK3 (P-RIPK3), UACA, and cleaved caspase-1 was up-regulated, while the expression of CASP1 and UNC5B was down-regulated. The expression of ZBP1 and BMF increased only during the development of ALF, and there was no significant change in the end stage. Immunofluorescence of mouse liver tissue showed that macrophages expressed all seven markers. Western blot results showed that pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis were always involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/ d-galactosamine (d-gal)-induced ALF mice. The ALF cell model showed that bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) form PANoptosomes after LPS stimulation. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that PANoptosis of macrophages promotes the development of ALF. The seven new ALF biomarkers identified and validated in this study may contribute to further investigation of diagnostic markers or novel therapeutic targets of ALF.
泛凋亡具有焦亡、凋亡和坏死性凋亡的特征。尽管大量研究已证实各类型细胞的死亡在急性肝衰竭(ALF)中发挥着不同作用,但对它们间的互作关注较少。本研究旨在探讨泛凋亡在ALF中的作用,并挖掘可作为预防或治疗ALF的新靶点。本研究首先从基因表达综合数据库(GEO)中下载三个与ALF相关的数据集(GSE14668、GSE62029和GSE74000),从中筛选差异表达基因(DEGs),并通过加权基因共表达网络分析(WGCNA)对上述基因和泛凋亡相关基因集取交集得到枢纽基因;通过基因本体论(GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)、蛋白质-蛋白质互作(PPI)和基因集富集分析(GSEA)确定枢纽基因功能;最后利用ALF小鼠和细胞模型进行验证。结果表明,在ALF患者肝脏样本中,7个枢纽基因(BMF、BNIP3L、CASP1、RIPK3、UACA、UNC5B、ZBP1)表达水平均上调;在ALF小鼠模型中,BNIP3L、RIPK3、P-RIPK3、UACA和cleaved caspase-1表达上调,而CASP1和UNC5B的表达下调;ZBP-1和BMF的表达仅在造模过程中升高,终末期则无明显变化。小鼠肝组织免疫荧光显示,这7个枢纽基因在巨噬细胞中均有表达;western blot结果表明,在脂多糖(LPS)/ d-氨基半乳糖( d-gal)引起的ALF小鼠模型中,焦亡、凋亡和坏死性凋亡均有发生;ALF细胞模型实验显示,骨髓源巨噬细胞在LPS刺激后形成泛凋亡小体。综上,巨噬细胞的泛凋亡有可能加速ALF的进展,此外本研究鉴定并验证的7个ALF枢纽基因将有希望作为未来深入研究ALF的诊断标志物或新的治疗靶点。.
泛凋亡具有焦亡、凋亡和坏死性凋亡的特征。尽管大量研究已证实各类型细胞的死亡在急性肝衰竭(ALF)中发挥着不同作用,但对它们间的互作关注较少。本研究旨在探讨泛凋亡在ALF中的作用,并挖掘可作为预防或治疗ALF的新靶点。本研究首先从基因表达综合数据库(GEO)中下载三个与ALF相关的数据集(GSE14668、GSE62029和GSE74000),从中筛选差异表达基因(DEGs),并通过加权基因共表达网络分析(WGCNA)对上述基因和泛凋亡相关基因集取交集得到枢纽基因;通过基因本体论(GO)、京都基因与基因组百科全书(KEGG)、蛋白质-蛋白质互作(PPI)和基因集富集分析(GSEA)确定枢纽基因功能;最后利用ALF小鼠和细胞模型进行验证。结果表明,在ALF患者肝脏样本中,7个枢纽基因(BMF、BNIP3L、CASP1、RIPK3、UACA、UNC5B、ZBP1)表达水平均上调;在ALF小鼠模型中,BNIP3L、RIPK3、P-RIPK3、UACA和cleaved caspase-1表达上调,而CASP1和UNC5B的表达下调;ZBP-1和BMF的表达仅在造模过程中升高,终末期则无明显变化。小鼠肝组织免疫荧光显示,这7个枢纽基因在巨噬细胞中均有表达;western blot结果表明,在脂多糖(LPS)/
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Biomarker; Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO); PANoptosis; Therapeutic target.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of early Alzheimer's disease subclass and signature genes based on PANoptosis genes.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 22;15:1462003. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1462003. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39650656 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics identification and validation of pyroptosis-related gene for ischemic stroke.BMC Med Genomics. 2025 Mar 16;18(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12920-025-02119-2. BMC Med Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40091022 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals molecular characterization and immune landscape of PANoptosis-related genes in atherosclerosis.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun;73(6):961-978. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01877-6. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38587531
-
The regulation of the ZBP1-NLRP3 inflammasome and its implications in pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis).Immunol Rev. 2020 Sep;297(1):26-38. doi: 10.1111/imr.12909. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Immunol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32729116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
It's All in the PAN: Crosstalk, Plasticity, Redundancies, Switches, and Interconnectedness Encompassed by PANoptosis Underlying the Totality of Cell Death-Associated Biological Effects.Cells. 2022 Apr 29;11(9):1495. doi: 10.3390/cells11091495. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563804 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

