Evaluation of exploratory fluid biomarkers from a phase 1 senolytic trial in mild Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40274471
- PMCID: PMC12418413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurot.2025.e00591
Evaluation of exploratory fluid biomarkers from a phase 1 senolytic trial in mild Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
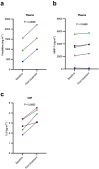
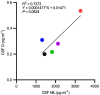
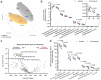
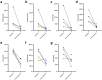
Senescent cell accumulation contributes to the progression of age-related disorders including Alzheimer's disease (AD). Clinical trials focused on cellular senescence are in early stages and have yet to establish reliable outcome measures reflecting senescent cell burden or response to senolytics, therapeutics that clear senescent cells. Results from the first open-label trial of senolytics, dasatinib plus quercetin (D + Q), in older adults (N = 5) with early AD demonstrated central nervous system penetration of dasatinib and favorable safety and tolerability. Herein, we present exploratory analyses of senescence and AD-associated analytes in blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and urine from this study in effort to guide biomarker development for future senolytic trials. Immunoassays, mass spectrometry and transcriptomics were performed and changes in analyte levels were assessed from baseline to post-treatment using paired t-tests. Targeted cytokine and chemokine analyses revealed increases in plasma fractalkine and MMP-7 and CSF IL-6 from baseline to post-treatment. Mass spectrometry indicated stable levels of amyloid β and tau proteins in CSF, unchanged urinary metabolites, and modest treatment-associated lipid profile changes. Targeted transcriptomic analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells indicated downregulation of inflammatory genes including FOS, FOSB, IL1β, IL8, JUN, JUNB, PTGS2. The levels and treatment responses of the analytes identified here may help inform trial design and outcomes for senolytic studies. Independent validation will be necessary to develop standardized biomarker panels across senolytic trials for AD. ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04063124.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Biofluids; Biomarkers; Clinical trial; Senolytics.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Ronald C. Petersen reports a relationship with University of Oxford, UpToDate, and Medscape that includes equity or stocks. Ronald C. Petersen reports personal stock in AbbVie. reports personal fees from Roche, Genetech, Eli Lilly, and Nestle, and no personal fees from Eisai, outside of the submitted work. Suzanne Craft reports a relationship with TD3 Therapeutics and Neurodegenerative Consortium that includes board membership. Suzanne Craft reports a relationship with vTv Therapeutics, Cylcerion, T3D Therapeutics, and Cognito Therapeutics, outside the submitted work that includes equity or stock. Randall J. Bateman reports a relationship with C2N Diagnostics and receives income from serving on the scientific advisory board as a co-founder. Randall J. Bateman has received research funding from Avid Radiopharmaceuticals, Janssen, Roche/Genentech, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Biogen, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Novartis. Mitzi M. Gonzales reports personal stock in Abbvie. James L. Kirkland and Tamara Tchkonia are co-investigators on a patent Treating Cognitive Decline and Other Neurodegenerative Conditions by Selectively Removing Senescent Cells from Neurological Tissue and a patent for Treating Cognitive Decline and Other Neurodegenerative Conditions by Selectively Removing Senescent Cells from Neurological Tissue that are held by Mayo Clinic with royalties paid to Mayo Clinic by Unity Biotechnologies. Dallin Mason, Samuel Johnson, and Suzanne Hendrix are employees of Pentara Corporation which provides consulting to over 30 pharmaceutical, biotech, non-profit, and academic groups doing clinical research in neurodegenerative disorders. Suzanne Hendrix is the founder, owner, and CEO of Pentara Corporation. Washington University has equity ownership interest in C2N Diagnostics and receives royalty income based on technology (Stable Isotope Labeling Kinetics, Blood Plasma Assay, and Methods of Diagnosing AD with Phosphorylation Changes) licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. Miranda Orr has patent Biosignature and Therapeutic Approach for Neuronal Senescence pending. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Update of
-
Evaluation of Exploratory Fluid Biomarker Results from a Phase 1 Senolytic Trial in Mild Alzheimer's Disease.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 8:rs.3.rs-3994894. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3994894/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Neurotherapeutics. 2025 Jul;22(4):e00591. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2025.e00591. PMID: 38496619 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Gorgoulis V., Adams P.D., Alimonti A., Bennett D.C., Bischof O., Bishop C., et al. Cellular senescence: defining a path forward. Cell. 2019;179(4):813–827. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

