A specific microbial consortium enhances Th1 immunity, improves LCMV viral clearance but aggravates LCMV disease pathology in mice
- PMID: 40274773
- PMCID: PMC12022176
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59073-x
A specific microbial consortium enhances Th1 immunity, improves LCMV viral clearance but aggravates LCMV disease pathology in mice
Abstract
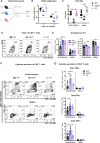
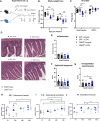
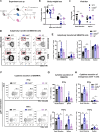
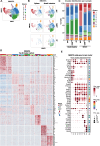
Anti-viral immunity can vary tremendously from individual to individual but mechanistic understanding is still scarce. Here, we show that a defined, low complex bacterial community (OMM12) but not the general absence of microbes in germ-free mice leads to a more potent immune response compared to the microbiome of specific-pathogen-free (SPF) mice after a systemic viral infection with LCMV Clone-13. Consequently, gnotobiotic mice colonized with OMM12 have more severe LCMV-induced disease pathology but also enhance viral clearance in the intestinal tract. Mechanistically, single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of adoptively transferred virus-specific T helper cells and endogenous T helper cells in the intestinal tract reveal a stronger pro-inflammatory Th1 profile and a more vigorous expansion in OMM12 than SPF mice. Altogether, our work highlights the causative function of the intestinal microbiome for shaping adaptive anti-viral immunity with implications for vaccination strategies and anti-cancer treatment regimens.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

