Heterogeneity of morphometric similarity networks in health and schizophrenia
- PMID: 40274815
- PMCID: PMC12022303
- DOI: 10.1038/s41537-025-00612-2
Heterogeneity of morphometric similarity networks in health and schizophrenia
Abstract
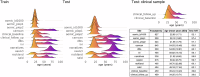
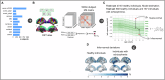
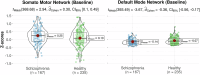
Reduced structural network connectivity is proposed as a biomarker for chronic schizophrenia. This study assessed regional morphometric similarity as an indicator of cortical inter-regional connectivity, employing longitudinal normative modeling to evaluate whether decreases are consistent across individuals with schizophrenia. Normative models were trained and validated using data from healthy controls (n = 4310). Individual deviations from these norms were measured at baseline and follow-up, and categorized as infra-normal, normal, or supra-normal. Additionally, we assessed the change over time in the total number of infra- or supra-normal regions for each individual. At baseline, patients exhibited reduced morphometric similarity within the default mode network compared to healthy controls. The proportion of patients with infra- or supra-normal values in any region at both baseline and follow-up was low (<6%) and similar to that of healthy controls. Mean intra-group changes in the number of infra- or supra-normal regions over time were minimal (<1) for both the schizophrenia and control groups, with no significant differences observed between them. Normative modeling with multiple timepoints enables the identification of patients with significant static decreases and dynamic changes of morphometric similarity over time and provides further insight into the pervasiveness of morphometric similarity abnormalities across individuals with chronic schizophrenia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Dr. Díaz-Caneja has received honoraria from Angelini and Viatris. Dr. Arango has been a consultant to or has received honoraria or grants from Acadia, Angelini, Gedeon Richter, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Otsuka, Roche, Sage, Servier, Shire, Schering-Plough, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Sunovion, and Takeda. Dr. Cahn has received unrestricted research grants from or served as an independent symposium speaker or consultant for Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lundbeck, Sanofi-Aventis, Janssen-Cilag, AstraZeneca, and Schering-Plough. The other authors report no financial relationships with commercial interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Heterogeneity of morphometric similarity networks in health and schizophrenia.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 18:2024.03.26.586768. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.26.586768. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Schizophrenia (Heidelb). 2025 Apr 24;11(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41537-025-00612-2. PMID: 38948832 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Jauhar, S., Johnstone, M. & McKenna, P. J. Schizophrenia. Lancet Lond. Engl.399, 473–486 (2022). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

