Vision transformer and deep learning based weighted ensemble model for automated spine fracture type identification with GAN generated CT images
- PMID: 40274849
- PMCID: PMC12022092
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98518-7
Vision transformer and deep learning based weighted ensemble model for automated spine fracture type identification with GAN generated CT images
Abstract
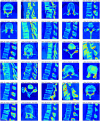
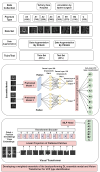
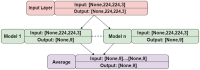
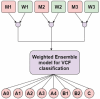
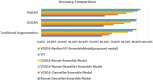
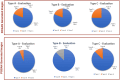
The most common causes of spine fractures, or vertebral column fractures (VCF), are traumas like falls, injuries from sports, or accidents. CT scans are affordable and effective at detecting VCF types in an accurate manner. VCF type identification in cervical, thoracic, and lumbar (C3-L5) regions is limited and sensitive to inter-observer variability. To solve this problem, this work introduces an autonomous approach for identifying VCF type by developing a novel ensemble model of Vision Transformers (ViT) and best-performing deep learning (DL) models. It assists orthopaedicians in easy and early identification of VCF types. The performance of numerous fine-tuned DL architectures, including VGG16, ResNet50, and DenseNet121, was investigated, and an ensemble classification model was developed to identify the best-performing combination of DL models. A ViT model is also trained to identify VCF. Later, the best-performing DL models and ViT were fused by weighted average technique for type identification. To overcome data limitations, an extended Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (DCGAN) and Progressive Growing Generative Adversarial Network (PGGAN) were developed. The VGG16-ResNet50-ViT ensemble model outperformed all ensemble models and got an accuracy of 89.98%. Extended DCGAN and PGGAN augmentation increased the accuracy of type identification to 90.28% and 93.68%, respectively. This demonstrates efficacy of PGGANs in augmenting VCF images. The study emphasizes the distinctive contributions of the ResNet50, VGG16, and ViT models in feature extraction, generalization, and global shape-based pattern capturing in VCF type identification. CT scans collected from a tertiary care hospital are used to validate these models.
Keywords: Computed tomography (CT) images; Deep convolutional generative adversarial network (DCGAN); Deep learning (DL); Ensemble deep learning model; Generative adversarial networks (GANs); Progressive growing generative adversarial network (PGGAN); Spine fracture; Vision transformer (ViT).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical clearance and informed consent statement: This retrospective study has been approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India with IEC number (IEC: 503/2020). Due to the retrospective nature of the study, the informed consent was waived and was approved by the Institutional Ethical Committee of Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I. & Hinton, G. E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM60, 84–90 (2017).
-
- Dosovitskiy, A. et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale (2021).
-
- Zheng, S. et al. Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 6881–6890 (2021).
-
- Li, G., Zhu, L., Liu, P. & Yang, Y. Entangled transformer for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision 8928–8937 (2019).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

