Identification of pivotal genes and regulatory networks associated with SAH based on multi-omics analysis and machine learning
- PMID: 40274967
- PMCID: PMC12022295
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98754-x
Identification of pivotal genes and regulatory networks associated with SAH based on multi-omics analysis and machine learning
Abstract
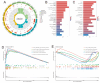
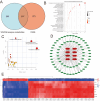
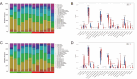
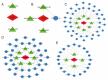
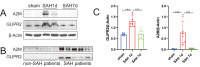
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a disease with high mortality and morbidity, and its pathophysiology is complex but poorly understood. To investigate the potential therapeutic targets post-SAH, the SAH-related feature genes were screened by the combined analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics of rat cortical tissues following SAH and proteomics of cerebrospinal fluid from SAH patients, as well as WGCNA and machine learning. The competitive endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and transcription factors (TFs) regulatory networks of the feature genes were constructed and further validated by molecular biology experiments. A total of 1336 differentially expressed proteins were identified, including 729 proteins downregulated and 607 proteins upregulated. The immune microenvironment changed after SAH and the changement persisted at SAH 7d. Through multi-omics and bioinformatics techniques, five SAH-related feature genes (A2M, GFAP, GLIPR2, GPNMB, and LCN2) were identified, closely related to the immune microenvironment. In addition, ceRNAs and TFs regulatory networks of the feature genes were constructed. The increased expression levels of A2M and GLIPR2 following SAH were verified, and co-localization of A2M with intravascular microthrombus was demonstrated. Multiomics and bioinformatics tools were used to predict the SAH associated feature genes confirmed further through the ceRNAs and TFs regulatory network development. These molecules might play a key role in SAH and may serve as potential biological markers and provide clues for exploring therapeutic options.
Keywords: A2M; Microthrombus; Multi-omics; Subarachnoid hemorrhage; WGCNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: All human procedures of the study were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University and performed according to the principles of Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki (Approval No. WDRY2023-K048). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardians for experiments involving human participants. All animal experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Wuhan University People’s Hospital (Ethical Approval Number for Animals:20230105A). All rats were executed prior to the experiment using high-dose sodium pentobarbital intraperitoneal injection. This experimental animal study complies with ARRIVE guidelines. All standard biosecurity and institutional safety procedures have been adhered to in all the experiment procedures in this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Machine learning and deep learning to identifying subarachnoid haemorrhage macrophage-associated biomarkers by bulk and single-cell sequencing.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(9):e18296. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18296. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38702954 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes and immune infiltration in peripheral blood biomarker analysis of delayed cerebral ischemia: Valproic acid as a potential therapeutic drug.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112408. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112408. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38897129
-
Multi-omics features of immunogenic cell death in gastric cancer identified by combining single-cell sequencing analysis and machine learning.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 18;14(1):21751. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73071-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39294296 Free PMC article.
-
Advance computational tools for multiomics data learning.Biotechnol Adv. 2024 Dec;77:108447. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108447. Epub 2024 Sep 7. Biotechnol Adv. 2024. PMID: 39251098 Review.
-
A comprehensive review of machine learning techniques for multi-omics data integration: challenges and applications in precision oncology.Brief Funct Genomics. 2024 Sep 27;23(5):549-560. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elae013. Brief Funct Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38600757 Review.
References
-
- Eagles, M. E., Tso, M. K., Macdonald, R. L., Cognitive & Impairment Functional outcome, and delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. World Neurosurg.124, e558–e562. 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.152 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Neifert, S. N. et al. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: the last decade. Transl. Stroke Res.12, 428–446. 10.1007/s12975-020-00867-0 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

