Mechanism of the effect of Piper crocatum extract on wound healing of Wistar rats post-excision mammary tumor based on IL-10 level, TGF-β1 expression, VEGF expression, Collagen density, and clinical features
- PMID: 40276181
- PMCID: PMC12017729
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i3.18
Mechanism of the effect of Piper crocatum extract on wound healing of Wistar rats post-excision mammary tumor based on IL-10 level, TGF-β1 expression, VEGF expression, Collagen density, and clinical features
Abstract
Background: The incidence of wound complications after breast cancer surgery is > 30%. Delayed wound healing increases the risk of systemic recurrence up to three-fold after excisional surgery for primary breast cancer. Patients with breast malignant tumors exhibit immune system dysfunction while T cells play a major role in the inflammatory process of wound healing. The time required to achieve wound closure depends on the severity of the wound. The content of Piper crocatum ethanol extract contains alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, steroids, and polyphenols. Flavonoid and polyphenol compounds are antioxidant, antidiabetic, anticancer, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory.
Aim: To determine whether P. crocatum extract increases interleukin-10 (IL-10) levels, TGF-β1 and VEGF expression, collagen density, and the clinical features of wounds, and how the mechanism works on wound healing of Wistar rats after excision of mammary tumors.
Methods: This study used 35 female Wistar rats, 30 mammary tumor models by injecting 3-5% benzopyrene as much as 50 mg/Kg.BW in 5 injections into the mammary glands/mammae every 2 days as much as 10 mg/kg.BW. Thirty rats were divided into 5 groups; red betel extract gel 50%, 25%, and 12.5%; povidone iodine group as a positive control; and carboxymethyl cellulose natrium (CMC na) group as a negative control, 5 normal wounds as controls. Treatment was given 2 times a day for 14 days.
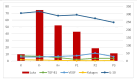
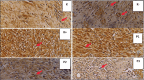
Results: Multiple linear regression results; P. crocatum extract decreased IL-10 levels by -0.64 (p = 0.025), decreased TGF-β1 expression -0.832 (p = 0.001), increased VEGF expression by 0.638 (p = 0.026), and decreased collagen density by -0.605 (p = 0.037) in mammary tumor post-excision rat wounds.
Conclusion: There is an effect of P. crocatum extract on the wound of Wistar rats after excision of mammary tumor by the mechanism of decreased IL-10 levels and TGF-β1 expression, increased VEGF expression, and decreased collagen density through increased VEGF expression is studied in this article.
Keywords: Collagen density; IL-10 level; Piper crocatum extract; TGF-β expression; VEGF expression.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
The N-butyl alcohol extract from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. flowers enhances healing potential on rat excisional wounds.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:291-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.016. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28088494
-
Topically applied substance P enhanced healing of open excision wound in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.042. Epub 2013 May 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23684543
-
Selenium added unripe carica papaya pulp extracts enhance wound repair through TGF-β1 and VEGF-a signalling pathway.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Oct 15;15:369. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0900-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26471293 Free PMC article.
-
Topical application of Acalypha indica accelerates rat cutaneous wound healing by up-regulating the expression of Type I and III collagen.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Jun 26;142(1):14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 Apr 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22521732
-
Targeting TGF-β/VEGF/NF-κB inflammatory pathway using the Polyphenols of Echinacea purpurea (L.) Moench to enhance wound healing in a rat model.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Apr;33(4):2151-2164. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01681-6. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40053247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alqathama A. Natural product as promising modulators of breast cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024 Available via https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2... . - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amadou A, Praud D, Coudon T, Deygas F, Grassot L, Faure E, Couvidat F., Caudeville J., Bessagnet B., Salizzoni P., Gulliver J., Leffondré K., Severi G., Mancini F.R., Fervers B. Risk of breast cancer associated with long-term exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) air pollution: evidence from the French E3N cohort study. Environ. Int. 2021;149:106399. - PubMed
-
- Barba D., León-Sosa A., Lugo P., Suquillo D., Torres F., Surre F., Trojman L., Caicedo A. Breast cancer, screening and diagnostic tools: all you need to know. Crit. Rev Oncol. Hematol. 2021;157:103174. - PubMed
-
- Başaran N, Evliyaoğlu O, Sucu V, Bulut L, Dikker O, Tezcan F, Vardar M. Changing of Uric Acid Levels by Age and Sex in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Investigations. 2017;21 7(1)
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
