Psychological distress and suicidal ideation in patients with depressive disorders: the chain mediation of psychological resilience and neuroticism
- PMID: 40276211
- PMCID: PMC12018043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2025.100325
Psychological distress and suicidal ideation in patients with depressive disorders: the chain mediation of psychological resilience and neuroticism
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Psychological distress and suicidal ideation in patients with depressive disorders: the chain mediation of psychological resilience and neuroticism" [International Journal of Nursing Studies 8 (2025) 100325].Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2025 Apr 29;8:100332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnsa.2025.100332. eCollection 2025 Jun. Int J Nurs Stud Adv. 2025. PMID: 40535789 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: Suicide in depressed patients has become a serious challenge in the field of public health. In-depth analyses of the relationship between psychological distress and suicidal ideation, as well as its intrinsic mechanisms, are of great clinical significance for the prevention of suicide in depressed patients. The objective of this study was twofold: firstly, to explore the intrinsic relationship between psychological distress and suicidal ideation in depth; and secondly, to further investigate the mediating roles of psychological resilience and neuroticism in this relationship.
Methods: In this study, a cross-sectional research design was employed to select 200 patients diagnosed with depression from a mental health centre in Shandong Province. This study utilised the abbreviated version of the Big Five Personality Inventory, the Simplified Scale of Psychological Resilience, the Suicidal Ideation Scale, and the Kessler Psychological Distress Scale to administer questionnaires to patients.
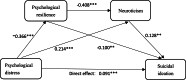
Results: Psychological distress has a direct predictive effect on suicidal ideation. In depressed patients, it also exerts an indirect effect on suicidal ideation via three pathways: the separate mediating effect of psychological resilience, the separate mediating effect of neuroticism, and the chain mediating effect of psychological resilience and neuroticism.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the results of this study elucidate the effect of psychological distress on suicidal ideation in depressed patients and its mechanism of action. Furthermore, they demonstrate the chain-mediated roles of psychological resilience and neuroticism in the relationship between psychological distress and suicidal ideation in depressed patients. Finally, they provide a new perspective for understanding suicidal ideation and preventing suicidal risk in depressed patients. Nevertheless, the present study was only able to measure the correlation between the variables; therefore, it is not yet possible to infer causality. In future, more precise prediction and intervention programmes for suicide risk in depressed patients can be explored in depth through longitudinal or experimental studies, etc.
Keywords: Chain mediation; Depression; Neuroticism; Psychological distress; Psychological resilience; Suicidal ideation.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Similar articles
-
The impact of psychological torque on suicidal ideation in elite athletes: the mediating role of psychological distress and the moderating role of sense of belonging.BMC Psychol. 2025 Jul 14;13(1):785. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02683-3. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40660337 Free PMC article.
-
Serial Multiple Mediation of Depressive Symptoms, Thwarted Belongingness, and Perceived Burdensomeness in the Relationship Between Personality Traits and Suicidal Ideation Among Nursing Students: A Cross-sectional Questionnaire Survey.Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2025 Aug;19(3):247-255. doi: 10.1016/j.anr.2025.03.005. Epub 2025 May 20. Asian Nurs Res (Korean Soc Nurs Sci). 2025. PMID: 40404096
-
Coping styles moderate stress pathways to suicidal ideation in clinic-based sample of Chinese adolescents with depression.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22963. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07409-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593087 Free PMC article.
-
[Neuroticism and suicidal thoughts: a meta-analytic study].Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2018 Aug 16;92:e201808049. Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2018. PMID: 30104562 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
A review and conceptual model of the association of Type D personality with suicide risk.J Psychiatr Res. 2021 Jun;138:291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.03.056. Epub 2021 Apr 7. J Psychiatr Res. 2021. PMID: 33882425
References
-
- J.H. Bolin, Hayes, F.A., Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. New York, NY: The Guilford Press, J Educ Meas 51 (2014) 335–337. 10.1111/jedm.12050. - DOI
-
- Chen J., Shi X.A. Investigation of suicidal ideation in patients with depression and its relationship with Family function: the mediating role of emotional regulation self-efficacy. China J. Health Psychol. 2024:1–12.
-
- Chu Z.S., Wang X., Cheng Y.Q., Xu X.F., Zhang F.F., Shen Z.L. Association between big five personality traits, childhood trauma and suicidal ideation in major depressive patients. Chin. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2023;49:396–401. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2023.07.003. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources