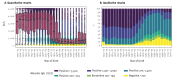
Seroprevalence against measles, Austria, stratified by birth years 1922 to 2024
- PMID: 40276882
- PMCID: PMC12023729
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.16.2400684
Seroprevalence against measles, Austria, stratified by birth years 1922 to 2024
Abstract
BackgroundVaccination programmes initiated in the early 1970s reduced the incidence of measles in Austria, which resulted in the interruption of endemic measles virus (MeV) circulation and the achievement of elimination status in 2018. However, large outbreaks occurred in 2023 and 2024.AimBy assessing MeV-specific IgG antibody levels, we analysed if immunity recently declined due to the COVID-19 pandemic, vaccine-induced immunity waned over long term or immunity gaps already pre-existed in the population.MethodsWe determined anti-MeV antibody levels in a retrospective dataset of 56,360 diagnostic samples (from 50,754 individuals) collected 2010-2024 and correlated antibody cutoffs to titres from a live-virus neutralisation test.ResultsIndividuals born before 1970 (n = 15,007) had antibody levels > 3,000 IU/L, persisting into higher age, and < 2% (n = 300) of them were seronegative. In contrast, individuals born after 1990 (n = 12,778) displayed seronegativity rates of 13-20% and lower median antibody concentrations in seropositive individuals (449-773 IU/L). In these individuals, antibody levels decreased noticeably between the ages of 2 and 10 years but remained stable between those aged 10 and 30 years. There was no significant difference in seronegativity rates at the age of 12-24 months in children born 2016-2019 and 2020-2022 (the years of the COVID-19 pandemic).ConclusionIn Austria, there are significant immunity gaps in individuals born after 1970, which pre-existed before the COVID-19 pandemic. Thus, young and middle-aged populations not immune against measles should be vaccinated to counteract a further decline of immunity at the population level and prevent outbreaks whenever MeV is imported.
Keywords: Austria; antibody; measles; measles–mumps–rubella (MMR) vaccine; seroprevalence; vaccines and immunisation; waning.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bundesministerium Soziales, Gesundheit, Pflege und Konsumentenschutz (BMSGPK). Jahresstatistik meldepflichtiger Infektionskrankheiten seit 1990. [Statistics and case numbers of notifiable diseases in Austria 2024]. Vienna: BMSGPK; 22 Apr 2025. German. Available from: https://www.sozialministerium.at/Themen/Gesundheit/Uebertragbare-Krankhe...
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Measles on the rise in the EU/EEA: considerations for public health response. Stockholm: ECDC; 16 Feb 2024. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/measles-eu-thre...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
