CrAssphage distribution analysis in an Amazonian river based on metagenomic sequencing data and georeferencing
- PMID: 40277368
- PMCID: PMC12093941
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.01470-24
CrAssphage distribution analysis in an Amazonian river based on metagenomic sequencing data and georeferencing
Abstract
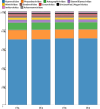
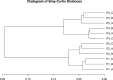
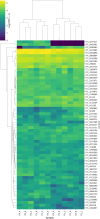
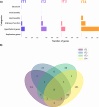
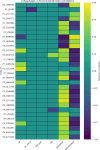
Viruses are the most abundant biological entities in all ecosystems of the world. Their ubiquity makes them suitable candidates for indicating fecal contamination in rivers. Recently, a group of Bacteroidetes bacteriophages named CrAssphages, which are highly abundant, sensitive, and specific to human feces, were studied as potential viral biomarkers for human fecal pollution in water bodies. In this study, we evaluated the presence, diversity, and abundance of viruses with a focus on crAssphages via metagenomic analysis in an Amazonian river and conducted correlation analyses on the basis of physicochemical and georeferencing data. Several significant differences in viral alpha diversity indexes were observed among the sample points, suggesting an accumulation of viral organisms in the river mouth, whereas beta diversity analysis revealed a significant divergence between replicates of the most downstream point (IT4) when compared to the rest of the samples, possibly due to increased human impact at this point. In terms of the presence of crAssphage, the analysis identified 61 crAssphage contigs distributed along the Itacaiúnas River. Moreover, our analysis revealed significant correlations between 19 crAssphage contigs and human population density, substantiating the use of these viruses as possible markers for human fecal pollution in the Itacaiúnas River. This study is the first to assess the presence of crAssphages in an Amazonian river, with results suggesting the potential use of these viruses as markers for human fecal pollution in the Amazon.
Importance: The Amazon biome is one of the most diverse ecosystems in the world and contains the most vast river network; however, the continuous advance of urban centers toward aquatic bodies exacerbates the discharge of pollutants into these water bodies. Fecal contamination contributes significantly to water pollution, and the application of an improved fecal indicator is essential for evaluating water quality. In this study, we evaluated the presence, diversity, and abundance of crAssphages in an Amazonian river and performed correlation analysis on the basis of physicochemical and georeferencing data to test whether crAssphages are viable fecal pollution markers. Our analysis revealed both the presence of crAssphages and their correlation with physicochemical data and showed significant correlations between the relative abundance of crAssphages and human density. These results suggest the potential use of these viruses as markers for water quality assessment in Amazonian rivers.
Keywords: Amazon; CrAssphage; biomarker; fecal contamination; freshwater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ellwanger JH, Kulmann-Leal B, Kaminski VL, Valverde-Villegas JM, Veiga A, Spilki FR, Fearnside PM, Caesar L, Giatti LL, Wallau GL, Almeida SEM, Borba MR, Hora VPD, Chies JAB. 2020. Beyond diversity loss and climate change: impacts of Amazon deforestation on infectious diseases and public health. An Acad Bras Cienc 92:e20191375. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202020191375 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

