Fast-Flu: RT-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a assisted one-step platform for rapid influenza B virus detection
- PMID: 40277382
- PMCID: PMC12131763
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00365-25
Fast-Flu: RT-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a assisted one-step platform for rapid influenza B virus detection
Abstract
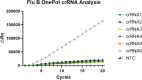
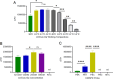
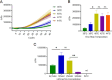
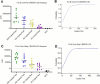
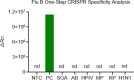
Influenza B virus (Flu B) is a prevalent respiratory pathogen responsible for seasonal influenza epidemics. Despite its clinical significance, there remains a lack of rapid and accurate diagnostic methods for Flu B detection. In this study, we developed a novel Flu B detection system, named Fast-Flu, by integrating reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification (RT-RPA) with the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated protein (Cas) system (CRISPR/Cas). Through optimization of reaction temperature and adjustment of Cas12a concentrations, we successfully balanced RPA amplification and CRISPR/Cas12a trans-cleavage activity, enabling the establishment of a one-step detection system. The one-step Fast-Flu system demonstrated the ability to specifically identify Flu B within 45 min, with a limit of detection of 58 copies per test. It eliminates the need for uncapping operations and minimizes the risk of cross-contamination, without cross-reactivity with other pathogens. When evaluated using 101 clinical throat swab samples, the one-step Fast-Flu system achieved a sensitivity of 56.25% and a specificity of 100% compared to the PCR-based method, with an overall concordance rate of 93.06% (94/101). The development of this one-step RT-RPA-CRISPR/Cas12a system represents a significant advancement in the rapid, convenient, and accurate detection of Flu B, highlighting its potential for clinical diagnosis. Furthermore, with future technical improvements to enhance sensitivity, this one-step RT-RPA-CRISPR assay holds promise as a versatile tool for the rapid nucleic acid detection of other RNA viruses.
Importance: Influenza B virus (Flu B) is a significant global health concern, and rapid, accurate pathogen diagnosis is crucial for effective influenza prevention and control. The integration of isothermal amplification methods with the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated protein (Cas) system has achieved high sensitivity and specificity for nucleic acid detection. Although CRISPR/Cas-based systems have been developed for influenza detection, existing platforms require the transfer of amplified products into the CRISPR/Cas12a detection system through uncapping operations, which increases the risk of cross-contamination. In this study, we developed a one-step reverse transcription recombinase polymerase amplification-CRISPR/Cas12a Flu B detection method using a one-pot detection system. By optimizing the reaction temperature and Cas12a concentration, we achieved a streamlined and contamination-free workflow. This innovative approach not only improves Flu B detection but also serves as a valuable reference for constructing CRISPR/Cas systems for the detection of other pathogens and targets, paving the way for broader applications in molecular diagnostics.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas12a; Fast-Flu; Flu B detection; RT-RPA; one-step.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

