Innovative Molecular Imprinting Sensor for Quick, Non-Invasive Cortisol Monitoring in Fish Welfare
- PMID: 40277519
- PMCID: PMC12025322
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15040204
Innovative Molecular Imprinting Sensor for Quick, Non-Invasive Cortisol Monitoring in Fish Welfare
Abstract
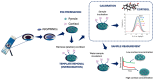
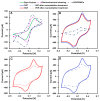
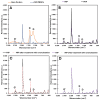
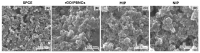
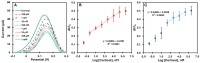
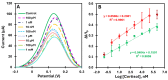
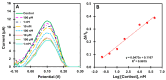
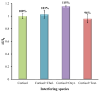
The assessment of fish welfare is crucial to prevent economic losses in aquaculture and ensure reliable results in research. A quick, non-invasive device to measure cortisol levels in fish farm water facilitates welfare evaluation and corrective actions when compromised. To address this need, an innovative sensor was developed using screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) functionalized with reduced graphene oxide/Prussian blue nanocubes (rGO/PBNCs) for direct selective detection of cortisol. A molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) was synthesized on rGO/PBNCs/SPCEs by electropolymerization (ELP) of pyrrole in the presence of cortisol. The polymerization solution was prepared by adding cortisol (5 mM) and pyrrole (0.3 M) to a DMF/PBS (1:4) solution (pH 7.4). Following ELP, the electrodes were washed with PBS, and pyrrole overoxidation was used to extract cortisol from the polymer matrix. For comparison purposes, a non-imprinted polymer (NIP) was also fabricated. The electrodes were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Raman spectroscopy to assess their morphological and chemical features. Under optimized conditions, the sensor showed a linear range from 0.1 nM to 0.1 mM in artificial saltwater. This sensor combines simplicity and affordability while providing reliable detection of chemical and biological compounds.
Keywords: European seabass; aquaculture; screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE); welfare assessment; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel biomimetic Prussian blue nanocubes-based biosensor for Tau-441 protein detection.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023 Mar 20;226:115251. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115251. Epub 2023 Jan 13. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2023. PMID: 36657353
-
Engineering electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer films for redox-integrated, reagent-free cortisol detection: The critical role of scan rate.Biosens Bioelectron. 2025 Oct 15;286:117623. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2025.117623. Epub 2025 May 25. Biosens Bioelectron. 2025. PMID: 40441108
-
An impedimetric molecularly-imprinted biosensor for Interleukin-1β determination, prepared by in-situ electropolymerization on carbon screen-printed electrodes.Bioelectrochemistry. 2019 Dec;130:107287. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Bioelectrochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31400567
-
D-mannitol sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer on electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide decorated with gold nanoparticles.Talanta. 2017 Apr 1;165:231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.12.040. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28153247
-
Flexible molecularly imprinted glucose sensor based on graphene sponge and Prussian blue.Bioelectrochemistry. 2024 Apr;156:108628. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2023.108628. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Bioelectrochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38104457 Review.
References
-
- Béné C., Barange M., Subasinghe R., Pinstrup-Andersen P., Merino G., Hemre G.-I., Williams M. Feeding 9 billion by 2050—Putting fish back on the menu. Food Secur. 2015;7:261–274.
-
- Aksnes D.W., Browman H.I. An overview of global research effort in fisheries science. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Du Conseil. 2015;73:1004–1011.
-
- Sloman K.A., Bouyoucos I.A., Brooks E.J., Sneddon L.U. Ethical considerations in fish research. J. Fish Biol. 2019;94:556–577. - PubMed
-
- Ellis T., Yildiz H.Y., López-Olmeda J., Spedicato M.T., Tort L., Øverli Ø., Martins C.I. Cortisol and finfish welfare. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2012;38:163–188. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

