Microbial Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors: Innovations from Design to Applications in Synthetic Biology
- PMID: 40277535
- PMCID: PMC12024804
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15040221
Microbial Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors: Innovations from Design to Applications in Synthetic Biology
Abstract
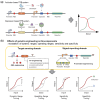
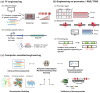
Transcription factor-based biosensors (TFBs) are powerful tools in microbial biosensor applications, enabling dynamic control of metabolic pathways, real-time monitoring of intracellular metabolites, and high-throughput screening (HTS) for strain engineering. These systems use transcription factors (TFs) to convert metabolite concentrations into quantifiable outputs, enabling precise regulation of metabolic fluxes and biosynthetic efficiency in microbial cell factories. Recent advancements in TFB, including improved sensitivity, specificity, and dynamic range, have broadened their applications in synthetic biology and industrial biotechnology. Computational tools such as Cello have further revolutionized TFB design, enabling in silico optimization and construction of complex genetic circuits for integrating multiple signals and achieving precise gene regulation. This review explores innovations in TFB systems for microbial biosensors, their role in metabolic engineering and adaptive evolution, and their future integration with artificial intelligence and advanced screening technologies to overcome critical challenges in synthetic biology and industrial bioproduction.
Keywords: dynamic metabolic control; genetic engineering; high-throughput screening (HTS); strain evolution; transcription factors (TFs)-based biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcription-Factor-based Biosensor Engineering for Applications in Synthetic Biology.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 May 21;10(5):911-922. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00252. Epub 2021 Apr 25. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 33899477 Review.
-
[Progress in transcription factor-based metabolite biosensors].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021 Mar 25;37(3):911-922. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200641. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 33783157 Review. Chinese.
-
Genetically encoded biosensors for microbial synthetic biology: From conceptual frameworks to practical applications.Biotechnol Adv. 2023 Jan-Feb;62:108077. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.108077. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Biotechnol Adv. 2023. PMID: 36502964 Review.
-
Genetically Encoded Biosensor Engineering for Application in Directed Evolution.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Oct 28;33(10):1257-1267. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2304.04031. Epub 2023 Jul 14. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37449325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Intelligent design of transcription factor-based biosensors].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025 Mar 25;41(3):1011-1022. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240603. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40170310 Review. Chinese.
References
-
- Rogers K. Recent advances in biosensor techniques for environmental monitoring. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2006;568:222–231. - PubMed
-
- Bidmanova S., Kotlanova M., Rataj T., Damborsky J., Trtilek M., Prokop Z. Fluorescence-based biosensor for monitoring of environmental pollutants: From concept to field application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016;84:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Ding D., Li J., Bai D., Fang H., Lin J., Zhang D. Biosensor-based monitoring of the central metabolic pathway metabolites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020;167:112456. - PubMed
-
- Higgins I., Lowe C. Introduction to the principles and applications of biosensors. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1987;316:3–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

