New Frontiers for the Early Diagnosis of Cancer: Screening miRNAs Through the Lateral Flow Assay Method
- PMID: 40277551
- PMCID: PMC12024991
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15040238
New Frontiers for the Early Diagnosis of Cancer: Screening miRNAs Through the Lateral Flow Assay Method
Abstract
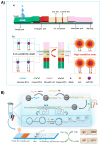
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which circulate in the serum and plasma, play a role in several biological processes, and their levels in body fluids are associated with the pathogenesis of various diseases, including different types of cancer. For this reason, miRNAs are considered promising candidates as biomarkers for diagnostic purposes, enabling the early detection of pathological onset and monitoring drug responses during therapy. However, current methods for miRNA quantification, such as northern blotting, isothermal amplification, RT-PCR, microarrays, and next-generation sequencing, are limited by their reliance on centralized laboratories, high costs, and the need for specialized personnel. Consequently, the development of sensitive, simple, and one-step analytical techniques for miRNA detection is highly desirable, particularly given the importance of early diagnosis and prompt treatment in cases of cancer. Lateral flow assays (LFAs) are among the most attractive point-of-care (POC) devices for healthcare applications. These systems allow for the rapid and straightforward detection of analytes using low-cost setups that are accessible to a wide audience. This review focuses on LFA-based methods for detecting and quantifying miRNAs associated with the diagnosis of various cancers, with particular emphasis on sensitivity enhancements achieved through the application of different labels and detection systems. Early, non-invasive detection of these diseases through the quantification of tailored biomarkers can significantly reduce mortality, improve survival rates, and lower treatment costs.
Keywords: biosensor; cancer; lateral flow assay; microRNA; point-of-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biosensors, microfluidics systems and lateral flow assays for circulating microRNA detection: A review.Anal Biochem. 2021 Nov 15;633:114406. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114406. Epub 2021 Oct 5. Anal Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34619101 Review.
-
Recent advances in lateral flow assays for MicroRNA detection.Clin Chim Acta. 2025 Feb 1;567:120096. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.120096. Epub 2024 Dec 15. Clin Chim Acta. 2025. PMID: 39681230 Review.
-
Quantum dots-labeled strip biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of microRNA based on target-recycled nonenzymatic amplification strategy.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Jan 15;87:931-940. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.043. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 27664413
-
A universal lateral flow assay for microRNA visual detection in urine samples.Talanta. 2023 Sep 1;262:124682. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124682. Epub 2023 May 20. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 37244240
-
[MicroRNA in Body Fluids - Development of the Novel Plat Form for Cancer Therapeutics and Diagnosis].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2018 Jun;45(6):899-905. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2018. PMID: 30026410 Japanese.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020.
-
- Mitchell P.S., Parkin R.K., Kroh E.M., Fritz B.R., Wyman S.K., Pogosova-Agadjanyan E.L., Peterson A., Noteboom J., O’Briant K.C., Allen A., et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:10513–10518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0804549105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

