Using Machine Learning for Analysis of Wideband Acoustic Immittance and Assessment of Middle Ear Function in Infants
- PMID: 40277580
- PMCID: PMC12023930
- DOI: 10.3390/audiolres15020035
Using Machine Learning for Analysis of Wideband Acoustic Immittance and Assessment of Middle Ear Function in Infants
Abstract
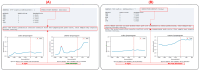
Objectives: Evaluating middle ear function is essential for interpreting screening results and prioritizing diagnostic referrals for infants with hearing impairments. Wideband Acoustic Immittance (WAI) technology offers a comprehensive approach by utilizing sound stimuli across various frequencies, providing a deeper understanding of ear physiology. However, current clinical practices often restrict WAI data analysis to peak information at specific frequencies, limiting its comprehensiveness.
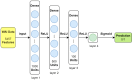
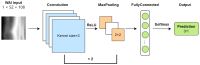
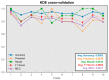
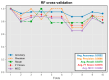
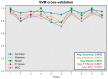
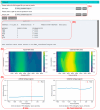
Design: In this study, we developed five machine learning models-feedforward neural network, convolutional neural network, kernel density estimation, random forest, and support vector machine-to extract features from wideband acoustic immittance data collected from newborns aged 2-6 months. These models were trained to predict and assess the normalcy of middle ear function in the samples.
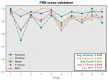
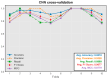
Results: The integrated machine learning models achieved an average accuracy exceeding 90% in the test set, with various classification performance metrics (accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, MCC) surpassing 0.8. Furthermore, we developed a program based on ML models with an interactive GUI interface. The software is available for free download.
Conclusions: This study showcases the capability to automatically diagnose middle ear function in infants based on WAI data. While not intended for diagnosing specific pathologies, the approach provides valuable insights to guide follow-up testing and clinical decision-making, supporting the early identification and management of auditory conditions in newborns.
Keywords: hearing of infants; machine learning; middle ear function; wideband acoustic immittance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

