Myoelectric Control in Rehabilitative and Assistive Soft Exoskeletons: A Comprehensive Review of Trends, Challenges, and Integration with Soft Robotic Devices
- PMID: 40277613
- PMCID: PMC12024817
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics10040214
Myoelectric Control in Rehabilitative and Assistive Soft Exoskeletons: A Comprehensive Review of Trends, Challenges, and Integration with Soft Robotic Devices
Abstract
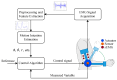
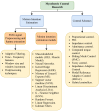
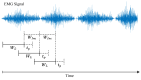
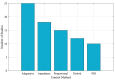
Soft robotic exoskeletons have emerged as a transformative solution for rehabilitation and assistance, offering greater adaptability and comfort than rigid designs. Myoelectric control, based on electromyography (EMG) signals, plays a key role in enabling intuitive and adaptive interaction between the user and the exoskeleton. This review analyzes recent advancements in myoelectric control strategies, emphasizing their integration into soft robotic exoskeletons. Unlike previous studies, this work highlights the unique challenges posed by the deformability and compliance of soft structures, requiring novel approaches to motion intention estimation and control. Key contributions include critically evaluating machine learning-based motion prediction, model-free adaptive control methods, and real-time validation strategies to enhance rehabilitation outcomes. Additionally, we identify persistent challenges such as EMG signal variability, computational complexity, and the real-time adaptability of control algorithms, which limit clinical implementation. By interpreting recent trends, this review highlights the need for improved EMG acquisition techniques, robust adaptive control frameworks, and enhanced real-time learning to optimize human-exoskeleton interaction. Beyond summarizing the state of the art, this work provides an in-depth discussion of how myoelectric control can advance rehabilitation by ensuring more responsive and personalized exoskeleton assistance. Future research should focus on refining control schemes tailored to soft robotic architectures, ensuring seamless integration into rehabilitation protocols. This review is a foundation for developing intelligent soft exoskeletons that effectively support motor recovery and assistive applications.
Keywords: electromyography; exoskeletons; motion intention estimation; myoelectric control; soft robotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


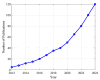
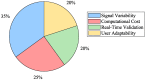
References
-
- du Plessis T., Djouani K., Oosthuizen C. A Review of Active Hand Exoskeletons for Rehabilitation and Assistance. Robotics. 2021;10:40. doi: 10.3390/robotics10010040. - DOI
-
- Masia L., Xiloyannis M., Khanh D.B., Wilson A.C., Contu S., Yongtae K.G. Rehabilitation Robotics. Elsevier; London, UK: 2018. Actuation for robot-aided rehabilitation: Design and control strategies; pp. 47–61. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

