Nanoscale Spatial Control over the Self-Assembly of Small Molecule Hydrogelators
- PMID: 40277725
- PMCID: PMC12026908
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11040289
Nanoscale Spatial Control over the Self-Assembly of Small Molecule Hydrogelators
Abstract
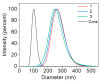
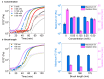
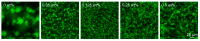
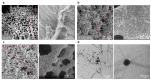
Spatial control over molecular self-assembly at the nano scale offers great potential for many high-tech applications, yet remains a challenging task. Here, we report a polymer brush-mediated strategy to confine the self-assembly of hydrazone-based hydrogelators exclusively at nanoparticle surfaces. The surfaces of these nanoparticles are grafted with negatively charged polyacrylic acid, which enrich protons that can catalyze the in situ formation and self-assembly of hydrazone-based gelators. We found that, with respect to the polymer lengths, the concentration of the nanoparticles presents more significant effects on the self-assembly process and the properties of the resultant hydrogels, including gelation time, stiffness, and network morphology. More interestingly, the hydrogel fibers are found to be formed specifically around the nanoparticles, demonstrating the directed nanoscale molecular self-assembly. This work demonstrates that triggering molecular self-assembly using catalysis can serve as an effective way to realize directed molecular self-assembly at the nano scale, which may serve as a powerful approach to improve many material properties, such as the mechanical properties of supramolecular materials as we found in this work.
Keywords: directed self-assembly; gelation; gels; small-molecular-weight-hydrogelators; supramolecular chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Directed Nanoscale Self-Assembly of Low Molecular Weight Hydrogelators Using Catalytic Nanoparticles.Adv Mater. 2018 May;30(21):e1707408. doi: 10.1002/adma.201707408. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Adv Mater. 2018. PMID: 29611239
-
Spatially Controlled Self-Assembly of Supramolecular Hydrogels Enabled by Light-Triggered Catalysis.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025 May;46(9):e2401156. doi: 10.1002/marc.202401156. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2025. PMID: 39918443
-
Localized self-assembly of macroscopically structured supramolecular hydrogels through reaction-diffusion.Soft Matter. 2024 Jun 20;20(24):4776-4782. doi: 10.1039/d4sm00467a. Soft Matter. 2024. PMID: 38842423
-
Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials.Chem Rev. 2015 Dec 23;115(24):13165-307. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00299. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Chem Rev. 2015. PMID: 26646318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface-Assisted Self-Assembly Strategies Leading to Supramolecular Hydrogels.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Feb 5;57(6):1448-1456. doi: 10.1002/anie.201708629. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29044982 Review.
References
-
- Ariga K., Ji Q., Nakanishi W., Hill J.P., Aono M. Nanoarchitectonics: A new materials horizon for nanotechnology. Mater. Horiz. 2015;2:406–413. doi: 10.1039/C5MH00012B. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

