Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern and Mycobacteria Lung Diseases: A Case Series
- PMID: 40277955
- PMCID: PMC12026791
- DOI: 10.3390/idr17020028
Usual Interstitial Pneumonia Pattern and Mycobacteria Lung Diseases: A Case Series
Abstract
Background: Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a heterogeneous group of conditions that can cause fibrosis of the lung interstitium, resulting in respiratory failure and death. Patients with an ILD, particularly idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or connective tissue disease-associated ILDs (CTD-ILDs), are prone to develop chronic pulmonary infections such as tuberculosis (TB) and non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD).
Methods: This case series examines the management of three ILD patients with a usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern and concomitant NTM-PD or TB at National Institute for Infectious Diseases "Lazzaro Spallanzani" in Rome, Italy, over three years (2019-2022).
Results and conclusions: Multi-disciplinary discussion (MDD) was crucial to define the therapeutic approach due to the increased risk of side effects and drug interactions. Our work underscored how a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, enriched by MDD, is useful for optimizing the management and reducing drug-related adverse effects and interactions in ILD patients with cavitary lesions.
Keywords: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF); interstitial lung diseases (ILDs); non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease (NTM-PD); tuberculosis (TB); usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
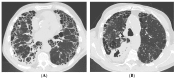
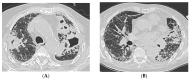
References
-
- Richeldi L., Collard H.R., Jones M.G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Lancet. 2017;389:1941–1952. - PubMed
-
- Raghu G., Remy-Jardin M., Richeldi L., Thomson C.C., Inoue Y., Johkoh T., Kreuter M., Lynch D.A., Maher T.M., Martinez F.J., et al. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (an Update) and Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis in Adults: An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022;205:e18–e47. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202202-0399st. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shu C.C., Chen P.S., Lin Z.H., Hsiao C.T., Kuo C.C., Chiang H.Y., Wu P.C. Prevalence and risk factors of non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary isolates and infection in interstitial lung disease associated with systemic autoimmune disease. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2024;42:1006–1014. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/c4oq1k. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

