Impact of Impaired Fasting Glucose on Musculoskeletal Pain Among Female-Dominated Healthcare Workers
- PMID: 40278301
- PMCID: PMC12028811
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm15040122
Impact of Impaired Fasting Glucose on Musculoskeletal Pain Among Female-Dominated Healthcare Workers
Abstract
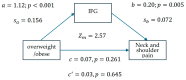
Introduction: In 2021, 10.5% of people aged 20-79 had diabetes, projected to rise to 12.2% by 2045, causing early deaths and straining healthcare systems. Musculoskeletal (MS) pain is common, affecting many workers and the general population. Prediabetes, notably impaired fasting glucose (IFG), is linked to increased MS pain risk. Objective: This study aims to assess IFG's impact on MS pain and specific pain sites to aid prevention strategies. Methods: This cross-sectional study used the '2023 Employee Occupational Safety and Health Management Database' from a Taichung hospital. It included health checks, demographics, living and work data, and MS pain surveys. Out of 2369 staff members contacted, 1039 valid responses were analyzed, excluding incomplete data, diabetes history, or fasting blood glucose levels above 125 mg/dL. Data on sex, age, marital status, coffee and alcohol consumption, sleep duration, exercise habits, height, weight, chronic diseases, profession, work hours, shift work, and education level were collected. Fasting blood glucose was verified using American Diabetes Association criteria (100-125 mg/dL). The Nordic Musculoskeletal Questionnaire (NMQ) measured MS pain frequency and severity, creating a pain degree index. Results: Overall, 21.17% had IFG. Participants were mostly female (85.18%), averaging 37.50 years. Neck and shoulder pain risk was linked to sex, coffee and alcohol consumption, sleep, exercise, chronic diseases, work hours, and IFG. Ankle pain risk was linked to coffee and alcohol consumption. IFG, coffee, alcohol, sleep under 6 h, chronic diseases, and work hours were independent risk factors for neck and shoulder pain. IFG was a risk factor for those without overweight or obesity. A mediation model tested IFG's indirect effect on neck and shoulder pain among overweight or obese individuals, showing that IFG mediates the relationship between being overweight or obese and increased neck and shoulder pain risk. Conclusions: Among female-dominated healthcare workers, IFG, daily coffee, recent alcohol consumption, less than 6 h of sleep, chronic diseases (excluding diabetes), and longer work hours are independent risk factors for neck and shoulder pain. IFG mainly affects these areas, increasing pain risk regardless of body weight. Healthy blood glucose levels are associated with a lack of musculoskeletal pain, suggesting a novel prevention approach needing further study.
Keywords: diabetes; impaired fasting glucose; musculoskeletal pain; obese; overweight; prediabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Effects of Frequent Coffee Drinking on Female-Dominated Healthcare Workers Experiencing Musculoskeletal Pain and a Lack of Sleep.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 22;13(1):25. doi: 10.3390/jpm13010025. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36675686 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between Marriage and Prediabetes among Healthcare Workers: Mediating Effect of Triglycerides.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Aug 30;60(9):1418. doi: 10.3390/medicina60091418. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39336459 Free PMC article.
-
Estimated number of adults with prediabetes in the US in 2000: opportunities for prevention.Diabetes Care. 2003 Mar;26(3):645-9. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.3.645. Diabetes Care. 2003. PMID: 12610015
-
Impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia: the current status on definition and intervention.Diabet Med. 2002 Sep;19(9):708-23. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2002.00835.x. Diabet Med. 2002. PMID: 12207806 Review.
-
Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with intermediate hyperglycaemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 29;10(10):CD012661. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012661.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30371961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atlas I. IDF Diabetes Atlas Ninth Edition 2019. 9th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2019.
-
- Davies M.J., Aroda V.R., Collins B.S., Gabbay R.A., Green J., Maruthur N.M., Rosas S.E., Del Prato S., Mathieu C., Mingrone G., et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetologia. 2022;65:1925–1966. doi: 10.1007/s00125-022-05787-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

