Secondary Metabolites from Croton Species and Their Biological Activity on Cell Cycle Regulators
- PMID: 40278345
- PMCID: PMC12029420
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo15040216
Secondary Metabolites from Croton Species and Their Biological Activity on Cell Cycle Regulators
Abstract
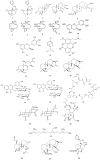
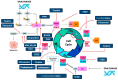
Plant-based traditional medicine integrates beliefs, knowledge, and practices to prevent and treat multiple diseases. Croton is a large and worldwide-spread genus belonging to Euphorbiaceae, a family well known for comprising many species with medicinal properties due to its high diversity of phytochemical constituents with biological activities. Among the various benefits of Croton species in traditional medicine, its use in cancer treatment has recently received significant attention from the scientific community. This review provides a general overview of different studies on the Croton genus in the research for alternative cancer treatments and the impact of its secondary metabolite catalog on cell cycle targets. Our analysis indicates that just under 30 secondary metabolites have been identified so far in latex and extracts obtained from leaves, twigs, or bark from 22 different Croton species. Based on standard assays using cell lines or human platelets, these molecules show multiple biological activities mainly compromising cell viability and cell cycle progression, supporting the ethnobotanical use of Croton species for cancer treatment. Several studies indicate that Croton metabolites target CDK-cyclin complexes and signaling routes that trigger apoptosis; however, further studies are needed to better understand the molecular mechanisms underlying Croton metabolites' effects and their accurate future applications in cancer treatment.
Keywords: apoptosis; cancer; cell cycle; plant metabolites; tropical plant species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A review of biological activities and phytochemistry of six ethnomedicinally important South African Croton species.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Nov 15;280:114416. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114416. Epub 2021 Jul 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34265381 Review.
-
Phytochemical study of the plant species Bidens pilosa L. (Asteraceae) and Croton floccosus (Euphorbiaceae).F1000Res. 2022 Jun 27;11:702. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.112653.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 36339983 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Dereplication of Trunk Bark Constituents of Croton sylvaticus and Molecular Docking of Terpenoids from Three Congolese Croton Species.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 1;26(9):4305. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094305. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362546 Free PMC article.
-
Leaf anatomy of two medicinal Croton species: Contribution to plant recognition.Microsc Res Tech. 2021 Aug;84(8):1685-1695. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23727. Epub 2021 Feb 13. Microsc Res Tech. 2021. PMID: 33580993
-
Chemical Constituents from Croton Species and Their Biological Activities.Molecules. 2018 Sep 12;23(9):2333. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092333. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30213129 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Villaseñor J.L. Checklist of the native vascular plants of México. Rev. Mex. Biodivers. 2016;87:559–902. doi: 10.1016/j.rmb.2016.06.017. - DOI
-
- Govaerts R., Frodin D.G., Radcliffe-Smith A., Carter S. World Checklist and Bibliography of Euphorbiaceae (with Pandaceae) The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; Richmond, UK: 2000. [(accessed on 29 May 2024)]. Available online: http://catalog.hathitrust.org/api/volumes/oclc/44041175.html.
-
- Webster G.L. A Provisional Synopsis of the Sections of the Genus Croton (Euphorbiaceae) Taxon. 1993;42:793–823. doi: 10.2307/1223265. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

