Role of Microbial Communities and Their Functional Gene in Anammox Process for Biodegradation of Bisphenol A and S in Pharmaceutical Wastewater
- PMID: 40278568
- PMCID: PMC12031610
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13040252
Role of Microbial Communities and Their Functional Gene in Anammox Process for Biodegradation of Bisphenol A and S in Pharmaceutical Wastewater
Abstract
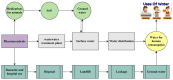
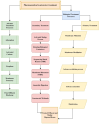
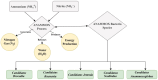
Substantial amounts of nitrogenous (N) compounds, as well as bisphenol A (BPA) and bisphenol S (BPS), contribute to the impurities of pharmaceutical contamination (PC) in wastewater, which have detrimental effects on the environment, humans, and aquaculture. The anammox processes is primarily used to treat wastewater contamination, in which certain microbial communities play a crucial role. In this regard, the present study focuses on microbial communities and the functional genes involved in the anammox process. Further, the current study highlights the secondary (biological) and tertiary (advanced) methods; these techniques are more effective solutions for PC treatment. Anammox bacteria are the primary drivers of the wastewater's ammonium and nitrite removal process. However, overall, 25 anammox species have been recognized between five important genera, including Anammoxoglobus, Anammoximicrobium, Brocadia, Kuenenia, and Jettenia, which are mainly found in activated sludge and marine environments. The group of bacteria called anammox has genes that encode enzymes such as hydrazine synthase (HZS), hydrazine dehydrogenase (HDH), nitrite oxidoreductase reductase (NIR), hydroxylamine oxidoreductase (HAO), and ammonium monooxygenase (AMO). The anammox process is responsible for developing about 30% to 70% N gases worldwide, making it a critical component of the nitrogen cycle as well. Therefore, this review paper also investigates the pathways of hydrazine, an intermediate in the anammox process, and discusses the potential way to significantly decrease the N-compound contamination from wastewater systems and the environmental effects of determined organic contaminants of BPA and BPS.
Keywords: advanced oxidation technologies; anaerobic; biphenyl A and S; pharmaceutical contamination; wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Wang Y., Shi Y., Xu X., Zhu Y. A Study on the Efficiency of Green Technology Innovation in Listed Chinese Water Environment Treatment Companies. Water. 2024;16:510. doi: 10.3390/w16030510. - DOI
-
- Gokulanathan V., Arun K., Priyadharshini P. Fresh and Hardened Properties of Five Non-Potable Water Mixed and Cured Concrete: A Comprehensive Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;309:125089.
-
- Patel M., Kumar R., Kishor K., Mlsna T., Pittman C.U., Jr., Mohan D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Systems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019;119:3510–3673. - PubMed
-
- Samal K., Trivedi S. A Statistical and Kinetic Approach to Develop a Floating Bed for the Treatment of Wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020;8:104102.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

