Effects of Benzo[k]fluoranthene at Two Temperatures on Viability, Structure, and Detoxification-Related Genes in Rainbow Trout RTL-W1 Cell Spheroids
- PMID: 40278618
- PMCID: PMC12031258
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13040302
Effects of Benzo[k]fluoranthene at Two Temperatures on Viability, Structure, and Detoxification-Related Genes in Rainbow Trout RTL-W1 Cell Spheroids
Abstract
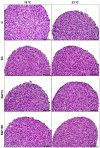
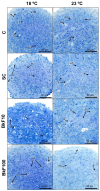
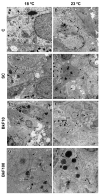
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and global warming impact aquatic ecosystems, eventually interacting. Monolayer (2D) cultures of cell lines, such as the rainbow trout liver RTL-W1, are employed for unveiling toxicological effects in fish. Nonetheless, three-dimensional (3D) models constitute an alternate paradigm, better emulating in vivo responses. Here, ultra-low attachment (ULA) plates were used to generate ten-day-old RTL-W1 spheroids for exposure to a control, a solvent control (0.1% DMSO) and the model PAH benzo[k]fluoranthene (BkF) at 10 and 100 nM and at 18 and 23 °C (thermal stress). After a 4-day exposure, spheroids were analyzed for viability (alamarBlue and lactate dehydrogenase), biometry (area, diameter and sphericity), histocytology (optical and electron microscopy), and mRNA levels of the detoxification-related genes cytochrome P450 (CYP)1A, CYP3A27, aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), glutathione S-transferase (GST), uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT), catalase (CAT), multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) and bile salt export protein (BSEP). Immunocytochemistry (ICC) was used to assess CYP1A protein expression. Neither temperature nor BkF exposure altered the spheroids' viability or biometry. BkF modified the cell's ultrastructure. The expression of CYP1A was augmented with both BkF concentrations, while AhR's increased at the higher concentration. The CYP1A protein showed a dose-dependent increase. Temperature and BkF concurrently modelled UGT's expression, which increased in the 100 nM condition at 23 °C. Conversely, CYP3A27, MRP2, and BSEP expressions lowered at 23 °C. CAT and GST mRNA levels were uninfluenced by either stressor. Overall, BkF and temperature impacted independently or interactively in RTL-W1 spheroids. These seem to be useful novel tools for studying the liver-related effects of temperature and PAHs.
Keywords: PAHs; benzo(k)fluoranthene; global warming; in vitro models; spheroids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
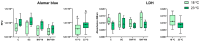



Similar articles
-
Unveiling the Effects of Two Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Two Temperatures on the Trout RTL-W1 Cell Line Expression of Detoxification-Related Target Genes.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jun 1;15(3):84. doi: 10.3390/jox15030084. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40558865 Free PMC article.
-
17α-Ethynylestradiol and Levonorgestrel Exposure of Rainbow Trout RTL-W1 Cells at 18 °C and 21 °C Mainly Reveals Thermal Tolerance, Absence of Estrogenic Effects, and Progestin-Induced Upregulation of Detoxification Genes.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;15(9):1189. doi: 10.3390/genes15091189. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336780 Free PMC article.
-
The Potentiating Effect of Graphene Oxide on the Arylhydrocarbon Receptor (AhR)-Cytochrome P4501A (Cyp1A) System Activated by Benzo(k)fluoranthene (BkF) in Rainbow Trout Cell Line.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 5;13(18):2501. doi: 10.3390/nano13182501. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764529 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of 3D and 2D in vitro models of the permanent fish liver cell line RTL-W1: Metabolic capabilities and responses to xenobiotics.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Dec;288:117327. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.117327. Epub 2024 Nov 16. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 39550873
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in farmed rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) processed by traditional flue gas smoking and by liquid smoke flavourings.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 May;46(5):1409-13. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.01.001. Epub 2008 Jan 10. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18262709 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Effects of Two Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Two Temperatures on the Trout RTL-W1 Cell Line Expression of Detoxification-Related Target Genes.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jun 1;15(3):84. doi: 10.3390/jox15030084. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 40558865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Méndez C., Simpson N., Johnson F., Birt A. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report (Full Volume) Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC; Geneva, Switzerland: 2023. - DOI
-
- Forster P.M., Smith C., Walsh T., Lamb W.F., Lamboll R., Hall B., Hauser M., Ribes A., Rosen D., Gillett N.P., et al. Indicators of Global Climate Change 2023: Annual update of key indicators of the state of the climate system and human influence. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2024;16:2625–2658. doi: 10.5194/essd-16-2625-2024. - DOI
-
- WMO WMO Confirms 2024 as Warmest Year on Record at About 1.55 °C Above Pre-Industrial Level. 2024. [(accessed on 10 March 2025)]. Available online: https://wmo.int/news/media-centre/wmo-confirms-2024-warmest-year-record-....
-
- Dupuy J.-L., Fargeon H., Martin-StPaul N., Pimont F., Ruffault J., Guijarro M., Hernando C., Madrigal J., Fernandes P. Climate change impact on future wildfire danger and activity in southern Europe: A review. Ann. For. Sci. 2020;77:35. doi: 10.1007/s13595-020-00933-5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

