Deciphering distinct genetic risk factors for FTLD-TDP pathological subtypes via whole-genome sequencing
- PMID: 40280976
- PMCID: PMC12032271
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59216-0
Deciphering distinct genetic risk factors for FTLD-TDP pathological subtypes via whole-genome sequencing
Abstract
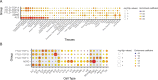
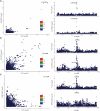
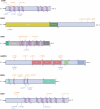
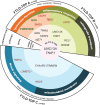
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration with neuronal inclusions of the TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (FTLD-TDP) is a fatal neurodegenerative disorder with only a limited number of risk loci identified. We report our comprehensive genome-wide association study as part of the International FTLD-TDP Whole-Genome Sequencing Consortium, including 985 patients and 3,153 controls compiled from 26 institutions/brain banks in North America, Europe and Australia, and meta-analysis with the Dementia-seq cohort. We confirm UNC13A as the strongest overall FTLD-TDP risk factor and identify TNIP1 as a novel FTLD-TDP risk factor. In subgroup analyzes, we further identify genome-wide significant loci specific to each of the three main FTLD-TDP pathological subtypes (A, B and C), as well as enrichment of risk loci in distinct tissues, brain regions, and neuronal subtypes, suggesting distinct disease aetiologies in each of the subtypes. Rare variant analysis confirmed TBK1 and identified C3AR1, SMG8, VIPR1, RBPJL, L3MBTL1 and ANO9, as novel subtype-specific FTLD-TDP risk genes, further highlighting the role of innate and adaptive immunity and notch signaling pathway in FTLD-TDP, with potential diagnostic and novel therapeutic implications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: S.J.H. serves on the scientific advisory board (SAB) of Proximity Therapeutics, Psy Therapeutics, Frequency Therapeutics, Souvien Therapeutics, Sensorium Therapeutics, 4 M Therapeutics, Ilios Therapeutics, Entheos Labs, Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, and the Kissick Family Foundation FTD Grant Program, none of whom were involved in the present study. S.J.H. has also received speaking or consulting fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, Merck, Regenacy Pharmaceuticals, Syros Pharmaceuticals, Juvenescence Life, as well as sponsored research or gift funding from AstraZeneca, JW Pharmaceuticals, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Vesigen Therapeutics, Compass Pathways, Atai Life Sciences, and Stealth Biotherapeutics. The funders had no role in the design or content of this article. ZKW serves as PI or Co-PI on Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (BHV4157-206), Vigil Neuroscience, Inc. (VGL101-01.002, VGL101-01.201, PET tracer development protocol, Csf1r biomarker and repository project, and ultra-high field MRI in the diagnosis and management of CSF1R-related adult-onset leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids and pigmented glia), and ONO-2808-03 projects/grants. He serves as Co-PI of the Mayo Clinic APDA Center for Advanced Research and as an external advisory board member for the Vigil Neuroscience, Inc., and as a consultant for Eli Lilly & Company and for NovoGlia, Inc. R.R. and I.R.M. receive royalties from progranulin-related patent. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Deciphering Distinct Genetic Risk Factors for FTLD-TDP Pathological Subtypes via Whole-Genome Sequencing.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 25:2024.06.24.24309088. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.24.24309088. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 25;16(1):3914. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59216-0. PMID: 38978643 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG013854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC008552/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG079850/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG077444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG063911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UG3/UH3 NS103870/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG066597/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC010367/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS084974/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG062268/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS092089/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072979/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG057195/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066511/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG091388/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG012300/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062422/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC012519/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH120794/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066509/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072977/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG062677/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG037491/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003949/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS094684/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010129/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG045390/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066468/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UG3 NS103870/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072972/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS085770/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

