Punicalagin relieves hepatic injury by antioxidation and enhancement of autophagy in diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 40280981
- PMCID: PMC12032207
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98044-6
Punicalagin relieves hepatic injury by antioxidation and enhancement of autophagy in diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
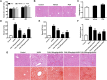
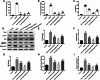
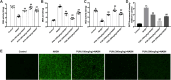
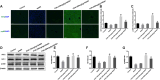
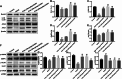
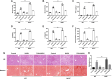
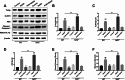
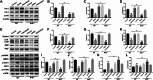
Hepatic injury induced by many factors play a central role in the pathogenesis of liver diseases. Punicalagin (PUN) is a major antioxidant polyphenolic compound extracted from pomegranates. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential role of PUN on liver injury induced by nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Therefore, the effects and mechanistic action of PUN on NASH mouse model induced by choline-deficient, L-amino acid- defined, high-fat (CDAAH) diet were investigated in vivo. Wild-type or nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) KO mice were fed with CDAAH diet to induce NASH and then treated with PUN (100, 300 or 500 mg kg- 1 day- 1) by gavage for 12 weeks. Blood and liver samples were collected to assess liver function, oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy pathological status. The results showed that 300 mg/kg PUN was the optimal concentration for relieving hepatic injury in NASH, characterized by decreased activities of serum alanine transaminase, aspartate aminotransferase, and liver lactate dehydrogenase activity and histopathological structural damage, and showed a hepatoprotective effect against NASH. PUN significantly reduced the level of liver inflammation and Txnip-NLRP3 signaling pathway in NASH mice. PUN reduced oxidative stress by reducing liver malondialdehyde levels and the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and increasing liver superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activity. PUN may also attenuate oxidative stress and induce autophagy through the p62/Nrf2 and AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 pathway. More importantly, we found that these protective effects of PUN were attributed to enhanced antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and autophagy activity, which was mediated by the activation of the Nrf2 pathway using Nrf2 KO mice. In summary, the present results indicate that PUN successfully relieved NASH-induced liver damage by upregulating Nrf2 signaling and autophagy.
Keywords: Autophagy; NASH; Nrf2; Oxidative stress; Punicalagin; Txnip-NLRP3 signaling.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Punicalagin Reversed the Hepatic Injury of Tetrachloromethane by Antioxidation and Enhancement of Autophagy.J Med Food. 2019 Dec;22(12):1271-1279. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2019.4411. Epub 2019 Nov 12. J Med Food. 2019. PMID: 31718395 Free PMC article.
-
Aloin protects mice from diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis via activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling.Food Funct. 2021 Jan 21;12(2):696-705. doi: 10.1039/d0fo02684k. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Food Funct. 2021. PMID: 33410857
-
Ezetimibe, an NPC1L1 inhibitor, is a potent Nrf2 activator that protects mice from diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2016 Oct;99:520-532. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27634173
-
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and mechanisms by which it is ameliorated by activation of the CNC-bZIP transcription factor Nrf2.Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Aug 1;188:221-261. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.06.226. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35728768 Review.
-
Hepatoprotective effects of diosmin: a narrative review.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):279-295. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03297-z. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39167171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Younossi, Z. M. et al. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. J. Hepatol.64, 73–84. 10.1002/hep.28431 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Surh, Y. J., Kundu, J. K. & Na, H. K. Nrf2 as a master redox switch in turning on the cellular signaling involved in the induction of cytoprotective genes by some chemopreventive phytochemicals. J. Planta Me. 74, 1526–1539. 10.1055/s-0028-1088302 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Zhu, H. et al. Nrf2 controls bone marrow stromal cell susceptibility to oxidative and electrophilic stress. J. Free Radic Biol. Med.41,132 – 43. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.03.02(2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

