Domain coupling in activation of a family C GPCR
- PMID: 40281344
- PMCID: PMC12394075
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01895-3
Domain coupling in activation of a family C GPCR
Abstract
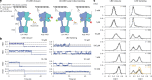
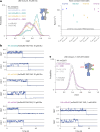
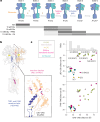
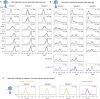
The G protein-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptors form homodimers and heterodimers with highly diverse responses to glutamate and varying physiological functions. We employ molecular dynamics, single-molecule spectroscopy and hydrogen-deuterium exchange to dissect the activation pathway triggered by glutamate. We find that activation entails multiple loosely coupled steps, including formation of an agonist-bound, pre-active intermediate whose transition to active conformations forms dimerization interface contacts that set efficacy. The agonist-bound receptor populates at least two additional intermediates en route to G protein-coupling conformations. Sequential transitions into these states act as 'gates', which attenuate the effects of glutamate. Thus, the agonist-bound receptor is remarkably dynamic, with low occupancy of G protein-coupling conformations, providing considerable headroom for modulation by allosteric ligands. Sequence variation within the dimerization interface, as well as altered conformational coupling in receptor heterodimers, may contribute to precise decoding of glutamate signals over broad spatial and temporal scales.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







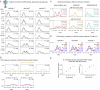

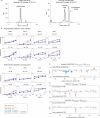

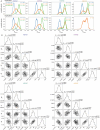
Update of
-
Domain coupling in activation of a family C GPCR.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 29:2024.02.28.582567. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.28.582567. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Chem Biol. 2025 Sep;21(9):1433-1443. doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-01895-3. PMID: 38464305 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R35GM149319/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- K99GM148823/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS)
- R35 GM149319/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CHE2137630/National Science Foundation (NSF)
- R01 NS119826/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1RF1MH123246/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- K99 GM148823/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS119826/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- RF1 MH123246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM116961/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Pecot/McKnight Endowment Fund for Neuroscience
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

