Real-time ultrasound-guided laryngeal mask assisted percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy versus bronchoscopy-guided percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy in critically ill patients: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40281453
- PMCID: PMC12023445
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03645-6
Real-time ultrasound-guided laryngeal mask assisted percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy versus bronchoscopy-guided percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy in critically ill patients: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
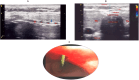
Background: Percutaneous dilatational tracheostomy (PDT) is a common procedure for mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit (ICU). This study compared the real-time ultrasound-guided PDT using a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) with the standard bronchoscopy-guided PDT technique in ICU patients requiring elective tracheostomy.
Methods: This randomized controlled study was conducted at Ain Shams University Hospital's Critical Care Department from December 4th, 2021, to December 3rd, 2022. The study population included 60 critically ill patients admitted to the ICU. Thirty patients were randomly assigned to the real-time ultrasound-guided LMA-assisted group, and 30 patients were randomly assigned to the bronchoscopy-guided technique. The primary study outcome was the procedure time, and the secondary outcomes included procedure-related complications rate and cost-effectiveness.
Results: The real-time ultrasound-guided LMA-assisted group had significantly shorter procedure time (median 17 [IQR: 15-20] min vs. 35 [IQR: 28-39] min, p < 0.001) and lower equipment damage (0% vs. 20%, p = 0.024) during the procedure compared to the bronchoscopy-guided group. Additionally, the cost of tracheostomy was significantly lower in the real-time ultrasound-guided LMA-assisted group (median: 300 vs. 800 USD, p < 0.001). The real-time ultrasound-guided LMA group had a lower major complications rate than the bronchoscopy-guided group (36.7%) vs. 3.3%, p = 0.002).
Conclusions: The study demonstrated that real-time ultrasound-guided LMA-assisted PDT had shorter procedure time, reduced equipment damage, lower costs, and was associated with lower complications when compared to the bronchoscopy-guided technique. These findings suggest that ultrasound guidance can enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of PDT procedures.
Keywords: Bleeding; Bronchoscopy-guided tracheostomy; Complications; Critically ill patients; Intensive care unit; Laryngeal mask airway; Percutaneous dilutional tracheostomy; Ultrasound-guided tracheostomy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The work was approved by the local Research Ethics Committee of Ain Shams University Faculty of Medicine (reference number: FMASU MD 164/2021) approved the protocol on December 3rd, 2021. The study was retrospectively registered in the ISRCTN registry (registration number ISRCTN14218985) on 02/07/2024. Informed consent: Informed written consent was obtained from the patients or their legal guardians in a private setting, where the study protocol was thoroughly explained to them. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wunsch H, et al. The epidemiology of mechanical ventilation use in the united States. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:1947–53. - PubMed
-
- Goligher E, Ferguson ND. Mechanical ventilation: epidemiological insights into current practices. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009;15:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Metnitz PG, et al. Epidemiology of mechanical ventilation: analysis of the SAPS 3 database. Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:816–25. - PubMed
-
- Heffner JE. The role of tracheotomy in weaning. Chest. 2001;120:s477–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

