Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting depression risk in patients with chronic kidney disease based on NHANES 2005-2018
- PMID: 40281636
- PMCID: PMC12023547
- DOI: 10.1186/s41043-025-00890-7
Development and validation of a nomogram for predicting depression risk in patients with chronic kidney disease based on NHANES 2005-2018
Abstract
Background: Depression is common among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with poor outcomes. This study aims to develop and validate a nomogram for predicting depression risk in patients with CKD.
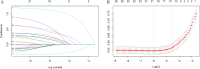
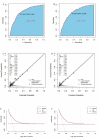
Methods: This cross-sectional study utilized data from the 2005-2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database. Participants were randomly divided into training and validation sets (7:3 ratio). A nomogram was developed based on predictors identified using Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) regression and multivariate logistic regression. Model performance was evaluated using ROC curves, calibration curves, and decision curve analysis.
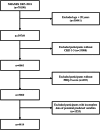
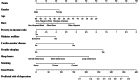
Results: A total of 4414 participants were included. Gender, age, race, poverty-to-income ratio, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, trouble sleeping, sleep hours, and smoking were included as predictors in the nomogram. The area under the curve (AUC) of the nomogram for predicting depression risk in patients with CKD was 0.785 (95% CI: 0.761-0.809) in the training set and 0.773 (95% CI: 0.737-0.810) in the validation set. The corrected C-index, calculated using bootstrap resampling, was 0.776, indicating good predictive performance. Calibration curves and decision curve analysis showed good calibration and clinical utility. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses further confirmed the robustness of the nomogram. A web-based risk calculator based on the nomogram was developed to enhance clinical applicability. A flowchart demonstrating the application of the nomogram for risk assessment and clinical decision-making in routine practice is provided.
Conclusions: This nomogram effectively predicts depression risk in patients with CKD and may serve as a user-friendly tool for the early identification of patients with CKD at high risk for depression using key demographic, comorbid, and lifestyle factors.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Cross-sectional study; Depression; NHANES; Nomogram; Questionnaire; Sociodemographic characteristics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The NHANES protocol was approved by the Ethics Review Committee of the NCHS, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Walklin CG, Young HML, Asghari E, Bhandari S, Billany RE, Bishop N, et al. The effect of a novel, digital physical activity and emotional well-being intervention on health-related quality of life in people with chronic kidney disease: trial design and baseline data from a multicentre prospective, wait-list randomised controlled trial (kidney BEAM). BMC Nephrol. 2023;24(1):122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kandemir I, Gudek K, Sahin AY, Aksakal MT, Kucuk E, Yildirim ZNY, et al. Association of problems, coping styles, and preferred online activity with depression, anxiety, and other psychological disorders in Turkish adolescents diagnosed with chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024;39(9):2779–88. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

