A maize landrace introgression library reveals a negative effect of root-to-shoot ratio on water-use efficiency
- PMID: 40281664
- PMCID: PMC12032046
- DOI: 10.1002/tpg2.70036
A maize landrace introgression library reveals a negative effect of root-to-shoot ratio on water-use efficiency
Abstract
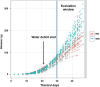
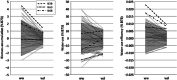
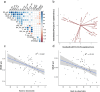
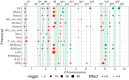
Novel sources of genetic variability for water-use efficiency (WUE) are needed in order to breed varieties more suitable to sustainable cropping systems. Here, a maize (Zea mays L.) introgression library of the landrace Gaspé Flint into the reference line B73 was characterized in high-throughput phenotyping platforms, both in well-watered and moderate water-deficit conditions, for water use, WUE, and root and shoot growth. Traits heritability ranged from 0.77 to 0.93. The introgression of Gaspé Flint chromosome segments into the B73 genome significantly altered several traits. Some introgression lines exhibited a faster shoot biomass accumulation than B73, resulting in higher WUE at the expense of root growth. Quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping identified seven major QTL clusters affecting shoot growth and WUE, two of which overlapped, with opposite effects, with QTLs for root biomass known to include root developmental genes. These results support the non-intuitive hypothesis that reduced root-to-shoot ratio positively affects maize WUE.
© 2025 The Author(s). The Plant Genome published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Crop Science Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bates, D. , Mächler, M. , Bolker, B. , & Walker, S. (2015). Fitting Linear Mixed‐Effects Models using lme4. Journal of Statistical Software, 67(1), 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 - DOI
-
- Bohn, M. , Novais, J. , Fonseca, R. , Tuberosa, R. , & Grift, T. E. (2006). Genetic evaluation of root complexity in maize. Acta Agronomica Hungarica, 54, 291–303. 10.1556/AAgr.54.2006.3.3 - DOI
-
- Bradbury, P. J. , Zhang, Z. , Kroon, D. E. , Casstevens, T. M. , Ramdoss, Y. , & Buckler, E. S. (2007). TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics, 23, 2633–2635. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

