Novel Tissue Engineering Scaffolds in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury-A Bibliometric Study
- PMID: 40281707
- PMCID: PMC12025192
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12040347
Novel Tissue Engineering Scaffolds in the Treatment of Spinal Cord Injury-A Bibliometric Study
Abstract
Objective: Because of the evolving nature of tissue engineering scaffolds in the treatment of spinal cord injury (SCI), the current study was carried out to evaluate the research productivity of tissue engineering scaffolds in the treatment of SCI.
Methods: Studies published from 2000 to 2025 were retrieved from the Web of Science core collection with topics of spinal cord injury and tissue engineering scaffolds. The data were analyzed and visualized using the VOSviewer network analysis software.
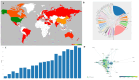
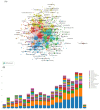
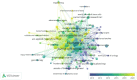
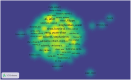
Results: Among 1542 articles analyzed, annual publications surged from 2000 to 2019, stabilizing thereafter. The U.S., China, and Canada led in productivity, with Northwestern University and the Biomaterials journal being top contributors. Keyword analysis revealed research hotspots such as functional recovery, axonal regeneration, stem cells, and hydrogels. Notably, hydrogels embedded with genetically engineered cells emerged as a pivotal trend, reflecting a shift toward biomimetic and combinatorial therapies. Collaboration networks highlighted intensified partnerships between Chinese and North American institutions, signaling global interdisciplinary efforts.
Conclusions: This study provides the first bibliometric roadmap for tissue engineering scaffolds in SCI, identifying key trends, influential entities, and underexplored areas. The rise in hydrogels and international collaborations underscores opportunities for targeted research. These findings guide researchers in prioritizing high-impact journals, fostering partnerships, and advancing novel scaffold designs to bridge translational gaps in SCI treatment.
Keywords: axonal regeneration; bibliographic study; cell transplantation; hydrogels; spinal cord injury; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yekaninejad M.S., Derakhshanrad N., Kazemi E., Derakhshanrad A., Saberi H. Influential factors for final neurorehabilitation outcome scores in patients with spinal cord injury: A longitudinal cohort study. J. Neurorestoratol. 2024;12:100117. doi: 10.1016/j.jnrt.2024.100117. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

