SwinDAF3D: Pyramid Swin Transformers with Deep Attentive Features for Automated Finger Joint Segmentation in 3D Ultrasound Images for Rheumatoid Arthritis Assessment
- PMID: 40281750
- PMCID: PMC12025309
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering12040390
SwinDAF3D: Pyramid Swin Transformers with Deep Attentive Features for Automated Finger Joint Segmentation in 3D Ultrasound Images for Rheumatoid Arthritis Assessment
Abstract
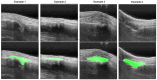
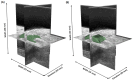
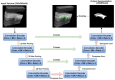
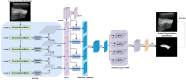
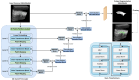
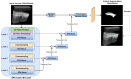
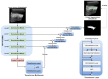
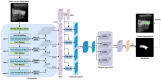
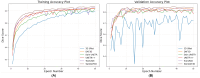
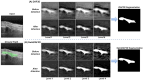
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that can cause severe joint damage and functional impairment. Ultrasound imaging has shown promise in providing real-time assessment of synovium inflammation associated with the early stages of RA. Accurate segmentation of the synovium region and quantification of inflammation-specific imaging biomarkers are crucial for assessing and grading RA. However, automatic segmentation of the synovium in 3D ultrasound is challenging due to ambiguous boundaries, variability in synovium shape, and inhomogeneous intensity distribution. In this work, we introduce a novel network architecture, Swin Transformers with Deep Attentive Features for 3D segmentation (SwinDAF3D), which integrates Swin Transformers into a Deep Attentive Features framework. The developed architecture leverages the hierarchical structure and shifted windows of Swin Transformers to capture rich, multi-scale and attentive contextual information, improving the modeling of long-range dependencies and spatial hierarchies in 3D ultrasound images. In a six-fold cross-validation study with 3D ultrasound images of RA patients' finger joints (n = 72), our SwinDAF3D model achieved the highest performance with a Dice Score (DSC) of 0.838 ± 0.013, an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 0.719 ± 0.019, and Surface Dice Score (SDSC) of 0.852 ± 0.020, compared to 3D UNet (DSC: 0.742 ± 0.025; IoU: 0.589 ± 0.031; SDSC: 0.661 ± 0.029), DAF3D (DSC: 0.813 ± 0.017; IoU: 0.689 ± 0.022; SDSC: 0.817 ± 0.013), Swin UNETR (DSC: 0.808 ± 0.025; IoU: 0.678 ± 0.032; SDSC: 0.822 ± 0.039), UNETR++ (DSC: 0.810 ± 0.014; IoU: 0.684 ± 0.018; SDSC: 0.829 ± 0.027) and TransUNet (DSC: 0.818 ± 0.013; IoU: 0.692 ± 0.017; SDSC: 0.815 ± 0.016) models. This ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness of combining a Swin Transformers feature pyramid with a deep attention mechanism, improving the segmentation accuracy of the synovium in 3D ultrasound. This advancement shows great promise in enabling more efficient and standardized RA screening using ultrasound imaging.
Keywords: 3D ultrasound; automated 3D segmentation; deep attentive features; pyramid Swin transformers; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Qiu, J.; Karageorgos, G.; Ghose, S.; Dentinger, A. and Mills, D. are employees of GE HealthCare. Yang, Z. is an employee of GE Vernova.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automatic segmentation and volume measurement of anterior visual pathway in brain 3D-T1WI using deep learning.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 28;12:1530361. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1530361. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40357297 Free PMC article.
-
CIS-UNet: Multi-class segmentation of the aorta in computed tomography angiography via context-aware shifted window self-attention.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2024 Dec;118:102470. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2024.102470. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2024. PMID: 39579454
-
Automated Deep Learning-Based Finger Joint Segmentation in 3-D Ultrasound Images With Limited Dataset.Ultrason Imaging. 2025 Jan;47(1):14-23. doi: 10.1177/01617346241277178. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Ultrason Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39295443
-
Robust Automated Mouse Micro-CT Segmentation Using Swin UNEt TRansformers.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;11(12):1255. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11121255. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768073 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient brain tumor segmentation using Swin transformer and enhanced local self-attention.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Feb;19(2):273-281. doi: 10.1007/s11548-023-03024-8. Epub 2023 Oct 5. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 37796413 Review.
References
-
- Dougados M., Devauchelle-Pensec V., François Ferlet J., D’Agostino M.A., Backhaus M., Bentin J., Chalès G., Chary-Valckenaere I., Conaghan P., Wakefield R.J., et al. The ability of synovitis to predict structural damage in rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study between clinical examination and ultrasound. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013;72:665–671. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201469. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naredo E., Collado P., Cruz A., Palop M.J., Cabero F., Richi P., Carmona L., Crespo M. Longitudinal power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis: Predictive value in disease activity and radiologic progression. Arthritis Care Res. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2007;57:116–124. doi: 10.1002/art.22461. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

