Pathogenomic Insights into Piscirickettsia salmonis with a Focus on Virulence Factors, Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Identification, and Resistance Dynamics
- PMID: 40282010
- PMCID: PMC12024244
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15081176
Pathogenomic Insights into Piscirickettsia salmonis with a Focus on Virulence Factors, Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Identification, and Resistance Dynamics
Abstract
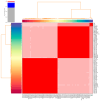
Effective control of bacterial infections remains a significant challenge in aquaculture. The marine bacterium Piscirickettsia salmonis (P. salmonis), responsible for piscirickettsiosis, causes widespread infections in various salmon species, leading to substantial mortality and economic losses. Despite efforts to genetically characterize P. salmonis, critical gaps persist in understanding its virulence factors, antimicrobial resistance genes, and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). This study addresses these gaps through a comparative analysis of the pan-genome and core genomes of 80 P. salmonis strains from different geographical regions and genogroups. P. salmonis had an open pan-genome consisting of 14,564 genes, with a core genome of 1257 conserved genes. Eleven virulence-related genes were identified in the pan-genome, categorized into five functional groups, providing new insights into the pathogenicity of P. salmonis. Unique SNPs were detected in four key genes (gyrA, dnaK, rpoB, and ftsZ), serving as robust molecular markers for distinguishing the LF and EM genogroups. Notably, AMR genes identified in four LF strains suggest evolutionary adaptations under selective pressure. Functional annotation of the core genomes using the gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) databases demonstrated conserved gene clusters linked to essential intracellular survival mechanisms and bacterial pathogenicity. These findings suggest a direct association between core genome features and variations in pathogenesis and host-pathogen interactions across genogroups. Phylogenetic reconstruction further highlighted the influence of AMR genes on strain divergence. Collectively, this study enhances the genomic understanding of P. salmonis and lays the groundwork for improved diagnostic tools and targeted therapeutics to manage piscirickettsiosis in aquaculture.
Keywords: SNPs; genomics; pathogenesis; piscirickettsiosis; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparative Pan-Genome Analysis of Piscirickettsia salmonis Reveals Genomic Divergences within Genogroups.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Oct 31;7:459. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00459. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29164068 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome comparative analysis of the pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis.Vet Microbiol. 2016 Nov 30;196:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.10.015. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Vet Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27939153
-
Development of a Multiplex PCR Assay for Genotyping the Fish Pathogen Piscirickettsia salmonis Through Comparative Genomics.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 11;12:673216. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.673216. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34177855 Free PMC article.
-
Piscirickettsiosis and Piscirickettsia salmonis in fish: a review.J Fish Dis. 2014 Mar;37(3):163-88. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12211. Epub 2013 Nov 26. J Fish Dis. 2014. PMID: 24279295 Review.
-
Vaccines for piscirickettsiosis (salmonid rickettsial septicaemia, SRS): the Chile perspective.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2017 Mar;16(3):215-228. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2017.1244483. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2017. PMID: 27690686 Review.
Cited by
-
Benchmarking pangenome dynamics and horizontal gene transfer in Mycobacterium marinum evolution.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 17;16:1537826. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1537826. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40600140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2022. - DOI
-
- Marinho-Neto F.A., Claudiano G.S., Yunis-Aguinaga J., Cueva-Quiroz V.A., Kobashigawa K.K., Cruz N.R., Moraes F.R., Moraes J.R. Morphological, microbiological and ultrastructural aspects of sepsis by Aeromonas hydrophila in Piaractus mesopotamicus. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0222626. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222626. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Iversen A., Asche F., Hermansen Ø., Nystøyl R. Production cost and competitiveness in major salmon farming countries 2003–2018. Aquaculture. 2020;522:735089. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735089. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

