The Vital Roles of Agricultural Crop Residues and Agro-Industrial By-Products to Support Sustainable Livestock Productivity in Subtropical Regions
- PMID: 40282018
- PMCID: PMC12023990
- DOI: 10.3390/ani15081184
The Vital Roles of Agricultural Crop Residues and Agro-Industrial By-Products to Support Sustainable Livestock Productivity in Subtropical Regions
Abstract
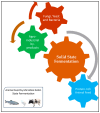
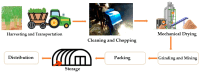
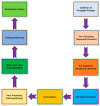
Sustainable livestock production is a critical component of global food security and environmental stewardship. Agricultural crop residues, such as cereal straws, stovers, and hulls, as well as agro-industrial by-products, including oilseed meals, distillery wastes, and fruit/vegetable processing residues, are generated in large quantities worldwide, and these residues can be used in the diet of the animals to reduce the feed production cost and sustainability. In this review, we found that the use of treated crop residues in the diet of animals increased the production performance without causing any side effects on their health. Additionally, we also noticed that using these crop residues also mitigates the methane production in ruminants and feed costs, particularly for harvesting the feed crops. Traditionally, these materials have often been underutilized or even disposed of improperly, leading to wastage of valuable nutrients and potential environmental pollution. By incorporating these materials into animal feed formulations, livestock producers can benefit from several key advantages. The review further discusses the challenges and considerations involved in the effective utilization of these alternative feed resources, such as variability in nutrient composition, anti-nutritional factors, and the need for appropriate preprocessing and formulation strategies. Emerging technologies and innovative approaches to optimize the integration of crop residues and by-products into sustainable livestock production systems and also reduce global warming, particularly methane, CO2 and other particles that affect the environment after burning these crop residues, are also highlighted. By synthesizing the current knowledge and exploring the multifaceted benefits, this review underscores the vital roles that agricultural crop residues and agro-industrial by-products can play in fostering the sustainability and resilience of livestock production, ultimately contributing to global food security and environmental stewardship.
Keywords: agriculture crop residues; agro-industrial by-products; crop residue utilization; sustainable livestock production; waste-to-feed.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors confer that there is no conflicts of interest in this article.
Figures



References
-
- Choe C., Cheon S., Gu J., Lim H. Critical aspect of renewable syngas production for power-to-fuel via solid oxide electrolysis: Integrative assessment for potential renewable energy source. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022;161:112398. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2022.112398. - DOI
-
- Awasthi M.K., Paul A., Kumar V., Sar T., Kumar D., Sarsaiya S., Liu H., Zhang Z., Binod P., Sindhu R. Recent trends and developments on integrated biochemical conversion process for valorization of dairy waste to value added bioproducts: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022;344:126193. - PubMed
-
- Theagarajan R., Malur Narayanaswamy L., Dutta S., Moses J.A., Chinnaswamy A. Valorisation of grape pomace (cv. Muscat) for development of functional cookies. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019;54:1299–1305. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14119. - DOI
-
- Ashokkumar V., Flora G., Venkatkarthick R., SenthilKannan K., Kuppam C., Stephy G.M., Kamyab H., Chen W.-H., Thomas J., Ngamcharussrivichai C. Advanced technologies on the sustainable approaches for conversion of organic waste to valuable bioproducts: Emerging circular bioeconomy perspective. Fuel. 2022;324:124313. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124313. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- YLXKZX-NND-012/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region First Class Discipline Research Special Project
- 2021ZD0013/Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Major Special Funding Project
- No. NMGIRT2412/Veterinary basic and cattle and sheep disease prevention and control technology research and innovation team project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

