Integrating Systems Thinking and Behavioural Science
- PMID: 40282025
- PMCID: PMC12023936
- DOI: 10.3390/bs15040403
Integrating Systems Thinking and Behavioural Science
Abstract
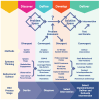
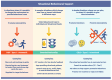
Traditional approaches to changing health behaviours have primarily focused on education and raising awareness, assuming that increased knowledge leads to better decisions. However, evidence suggests these methods often fail to result in sustained behavioural change. The dual-process theory of decision-making highlights that much of our behaviour is driven by automatic, intuitive processes, which educational interventions typically overlook. Compounding this challenge, behavioural research is often conducted on small groups, making it difficult to scale insights into broader societal issues, where behaviour is influenced by complex, interconnected factors. This review advocates for integrating behavioural science with systems approaches (including systems thinking and approaches to complex adaptive systems) as a more effective approach to resolving complex societal issues, such as public health, sustainability, and social equity. Behavioural science provides insights into individual decision-making, while systems approaches offer ways of understanding, and working with, the dynamic interactions and feedback loops within complex systems. The review explores the commonalities and differences between these two approaches, highlighting areas where they complement one another. Design thinking is identified as a useful structure for bridging behavioural science and systems thinking, enabling a more holistic approach to problem-solving. Though some ideological challenges remain, the potential for creating more effective, scalable solutions is significant. By leveraging the strengths of both behavioural science and systems thinking, one can create more comprehensive strategies to address the "wicked problems" that shape societal health and well-being.
Keywords: behaviour; change; complexity; design thinking; dual-process; multidisciplinary; nudge; public health; systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beer S. The viable system model: Its provenance, development, methodology and pathology. Journal of the Operational Research Society. 1984;35(1):7–25.
-
- Beerel A. Leadership and change management. SAGE Publications Ltd; 2009. - DOI
-
- Berger J., Efferson C., Vogt S. Tipping pro-environmental norm diffusion at scale: Opportunities and limitations. Behavioural Public Policy. 2023;7(3):581–606. doi: 10.1017/bpp.2021.36. - DOI
-
- Breslin G., Fakoya O., Wills W., Lloyd N., Bontoft C., Wellings A., Harding S., Jackson J., Barrett K., Wagner A. P., Miners L., Greco H. A., Brown K. E. Whole systems approaches to diet and healthy weight: A scoping review of reviews. PLoS ONE. 2024;19(3):e0292945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292945. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

