Online Captive: The Impact of Social Media Addiction on Depression and Anxiety-An SEM Approach to the Mediating Role of Self-Esteem and the Moderating Effects of Age and Professional Status
- PMID: 40282102
- PMCID: PMC12024447
- DOI: 10.3390/bs15040481
Online Captive: The Impact of Social Media Addiction on Depression and Anxiety-An SEM Approach to the Mediating Role of Self-Esteem and the Moderating Effects of Age and Professional Status
Abstract
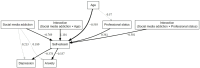
In the "era" in which social networks have become an integral part of everyday life, this study aims to analyze the impact of social network addiction on mental health, with a focus on the manifestation of anxiety and depression symptoms. The relationship analyzed on a batch of a Romanian adult population, explained by self-esteem and influenced by factors such as age and professional status, highlights the fact that all age categories and professional status can be affected by addiction to the online environment but with different degrees of intensity. The analyses carried out using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) suggest that young people and professionally inactive people are the categories with the highest degree of self-esteem impairment and with a high potential to manifest symptoms associated with depression and anxiety disorders, as a result of the intense use of social networks. The current study makes a significant contribution to the specialized literature, given the small volume of similar studies conducted on the adult population of Romania.
Keywords: anxiety; depression; professional status; self-esteem; social networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Similar articles
-
The impact of depression and anxiety on mobile phone addiction and the mediating effect of self-esteem.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 3;14(1):23004. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71947-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39362873 Free PMC article.
-
Social media addiction relationship with academic engagement in university students: The mediator role of self-esteem, depression, and anxiety.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 9;10(2):e24384. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24384. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293527 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Adolescent Internet Addiction on Sexual Online Victimization: The Mediating Effects of Sexting and Body Self-Esteem.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 16;18(8):4226. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084226. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33923552 Free PMC article.
-
Relationships between Depression, Fear of Missing Out and Social Media Addiction: The Mediating Role of Self-Esteem.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Jun 6;11(12):1667. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11121667. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372785 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioural modification interventions for medically unexplained symptoms in primary care: systematic reviews and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2020 Sep;24(46):1-490. doi: 10.3310/hta24460. Health Technol Assess. 2020. PMID: 32975190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Affizie G. How does social media exacerbate feelings of inadequacy and social comparison among young adults: A literature review. Zenodo; 2024. - DOI
-
- Akram M., Nasar A. A bibliometric analysis of radicalization through social media. Ege Akademik Bakis (Ege Academic Review) 2023;23(2):279–296. doi: 10.21121/eab.1166627. - DOI
-
- Alabri A. Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): The effects of the need to belong, perceived centrality, and fear of social exclusion. Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies. 2022;2022:4824256. doi: 10.1155/2022/4824256. - DOI
-
- Al Ahbabi A., Al Teneiji A., Al Shaer A., Al Jaberi G., ElSayary A. The effects of social media on self-esteem; Proceedings of the 28th World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics: WMSCI 2024; Virtual. September 10–13; 2024. pp. 185–192. - DOI
-
- Aldwin C. M., Yancura L., Lee H. Handbook of the psychology of aging. Elsevier; 2021. Stress, coping, and aging; pp. 275–286. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources