Parenting Stress and Its Influencing Factors Among Chinese Parents in Parent-Grandparent Co-Parenting Families: A Latent Profile Analysis
- PMID: 40282154
- PMCID: PMC12024202
- DOI: 10.3390/bs15040533
Parenting Stress and Its Influencing Factors Among Chinese Parents in Parent-Grandparent Co-Parenting Families: A Latent Profile Analysis
Abstract
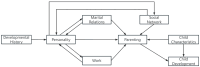
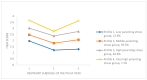
Guided by family systems theory and the parenting process model, this study aimed to identify distinct profiles of parenting stress and examine their associations with parental characteristics, social-contextual factors, and child factors. A sample of 303 parents of preschool children (52.5% boys, mean child age = 61.17 months) from six urban kindergartens in southern and northern China participated in this study. Latent profile analysis (LPA) identified four distinct parenting stress profiles: the low parenting stress profile (12.9%), middle parenting stress profile (39.3%), high parenting stress profile (40.6%), and very high parenting stress profile (7.2%). Multinomial logistic regression analysis revealed that these profiles were significantly associated with parenting self-efficacy, the parent-grandparent co-parenting relationship, the co-parenting structure, family income, and the child's gender. These findings advance our understanding of the heterogeneity of parenting stress within Chinese parent-grandparent co-parenting families and offer theoretical and practical implications for future research and the development of targeted family support interventions.
Keywords: latent profile analysis; parenting stress; parent–grandparent co-parenting; preschool children.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bidirectional Longitudinal Relations Between Parent-Grandparent Co-parenting Relationships and Chinese Children's Effortful Control During Early Childhood.Front Psychol. 2020 Feb 25;11:152. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00152. eCollection 2020. Front Psychol. 2020. PMID: 32158410 Free PMC article.
-
Perspectives on Stress, Parenting, and Children's Obesity-Related Behaviors in Black Families.Health Educ Behav. 2016 Dec;43(6):632-640. doi: 10.1177/1090198115620418. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Health Educ Behav. 2016. PMID: 26733488 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between parent and child latent eating profiles and the role of parental feeding practices.Appetite. 2024 Oct 1;201:107589. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2024.107589. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Appetite. 2024. PMID: 38977034
-
The effects of co-parenting/intergenerational co-parenting interventions during the postpartum period: A systematic review.Int J Nurs Stud. 2021 Jul;119:103951. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2021.103951. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Int J Nurs Stud. 2021. PMID: 34023796
-
A systematic review of parental burnout and related factors among parents.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 5;24(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17829-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38317118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abidin R. R. Introduction to the special issue: The stresses of parenting. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology. 1990a;19:298–301. doi: 10.1207/s15374424jccp1904_1. - DOI
-
- Abidin R. R. The parenting stress index-short form-test manual. Pediatric Psychology Press; 1990b. pp. 278–280.
-
- Abidin R. R. Parenting stress index (PSI) 3rd ed. Psychological Assessment Resources; 1995.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous