Long-Term Management and Monitoring of the Bladder After Spinal Cord Injury in a Rodent Model
- PMID: 40282238
- PMCID: PMC12024967
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14040373
Long-Term Management and Monitoring of the Bladder After Spinal Cord Injury in a Rodent Model
Abstract
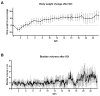
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a complex clinical condition with a wide range of permanent functional and neurological consequences. A prime factor limiting the patient's quality of life (QoL) is difficulties in bladder function. Chronic animal models that help to develop novel therapeutic strategies are highly demanded, but their availability is scarce and frequently accompanied by substantial limitations. We want to provide our detailed protocols that allow full reproducibility of a novel model for investigating both the acute and chronic condition, and give transparency regarding challenges. The preclinical animal model of female rats with mid-thoracic SCI contusion and a permanently implanted urinary catheter allowed the measuring of bladder function repetitively. Over a period of six months, data were collected weekly from the same, conscious individuals. To our knowledge, this is the first study that obtained a clinically relevant urodynamic dataset seamlessly from the acute to the chronic phase in rats with SCI. The ability to generate a complete data set from one single individual, rather than requiring multiple subjects, has the potential to markedly reduce the number of experimental animals, eliminate group differences, and give more flexibility for therapeutic intervention. Future projects could also benefit from the described optimizations in animal care.
Keywords: 3R; animal model; neurogenic bladder; neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (nLUTD); spinal cord injury (SCI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Costa P., Costa P., Perrouin-Verbe B., Perrouin-Verbe B., Colvez A., Colvez A., Didier J.P., Didier J.P., Marquis P., Marquis P., et al. Quality of life in spinal cord injury patients with urinary difficulties. Development and validation of QUALIVEEN. Eur. Urol. 2001;39:107–113. doi: 10.1159/000052421. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

