Advances in Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Extraction Methods and Pharmacological Effects
- PMID: 40282242
- PMCID: PMC12024818
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14040377
Advances in Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Extraction Methods and Pharmacological Effects
Abstract
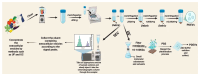
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are those with a double-membrane structure that contains proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and other biologically active substances that play an important role in cell-cell and cell-environment communication. They have also become an important mechanism for exchanging biologically active substances for cellular molecules. As many studies on EVs have been conducted, plant-derived extracellular vesicles (PDEVs) have also started attracting attention. The biological activity and stability of PDEVs are closely related to the extraction and separation methods, and choosing a separation method that meets the requirements of PDEVs is important. The extraction methods of PDEVs include ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, size-exclusion chromatography, etc. In recent years, it has been found through research that PDEVs possess biological properties, such as anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-infective properties, and that they show unique advantages as therapeutic agents and drug carriers. Therefore, we have collected the scientific literature related to EVs derived from more than a dozen fruits and vegetables, and summarized and analyzed their extraction, separation, and roles in disease treatment, aiming to provide reference and inspiration for the in-depth study of the efficacy of new drugs.
Keywords: anti-infective; anti-inflammatory; anticancer; extraction; plant-derived extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials