Integration of Microarray and Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data and Machine Learning Allows the Identification of Key Histone Modification Gene Changes in Spermatogonial Stem Cells
- PMID: 40282252
- PMCID: PMC12024924
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14040387
Integration of Microarray and Single-Cell RNA-Seq Data and Machine Learning Allows the Identification of Key Histone Modification Gene Changes in Spermatogonial Stem Cells
Abstract
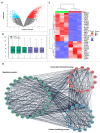
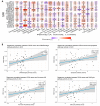
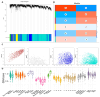
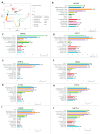
Histone modifications play a critical role in regulating gene expression and maintaining the functionality of spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs), which are essential for male fertility and spermatogenesis. In this study, we integrated microarray and single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) data to identify key histone modification gene changes associated with SSC function and aging. Through differential expression analysis, we identified 2509 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in SSCs compared to fibroblasts. Among these, genes involved in histone modification, such as KDM5B, SCML2, SIN3A, and ASXL3, were highlighted for their significant roles in chromatin remodeling and gene regulation. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks and gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis revealed critical biological processes such as chromatin organization, histone demethylation, and chromosome structure maintenance. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) further revealed three key modules of co-expressed genes related to spermatogonial aging. Additionally, ligand-receptor interaction scoring based on tumor microenvironment analysis suggested potential signaling pathways that could influence the stemness and differentiation of SSCs. Our findings provide new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying SSC aging, highlighting histone modification genes as potential therapeutic targets for preserving male fertility and improving SSC-culturing techniques. This study advances our understanding of histone modification in SSC biology and will serve as a valuable resource for future investigations into male fertility preservation.
Keywords: bioinformatics; gene ontology; germ cell; microarray; spermatogonia stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
It is declared by the remaining authors that there are no commercial or financial relationships that might conflict with this research.
Figures


References
-
- Aballa L., Chraa M., Louhab N., Kissani N. Extensive anaplastic multi-centric ependymoma in a young adult: Case report and literature review. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2023;59:67. doi: 10.1186/s41983-023-00663-1. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

