Evaluating the Effect of an Essential Oil Blend on the Growth and Fitness of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
- PMID: 40282302
- PMCID: PMC12024878
- DOI: 10.3390/biology14040437
Evaluating the Effect of an Essential Oil Blend on the Growth and Fitness of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
Abstract
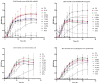
The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria has necessitated the exploration of alternative antimicrobial agents, particularly natural products like essential oils. This study investigated the antibacterial potential of a unique blend of four essential oils (EOB) across a gradient of concentrations (0.1 to 50%) against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria using an adapted broth microdilution method, minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs), and 24-h growth assays. The Gram-positive bacteria were Staphylococcus epidermidis and Bacillus subtilis, while the Gram-negative bacteria were Escherichia coli and Klebsiella aerogenes. The results demonstrated that the EOB exerted a concentration-dependent inhibitory effect on bacterial growth, with MICs determined at 25% for all the species tested. Growth curve analysis revealed that lower concentrations of the EOB (0.1 to 0.78%) allowed for normal bacterial proliferation, while at intermediate concentrations (1.56 to 3.13%), inconsistent trends in growth were exhibited. At higher concentrations (25 and 50%), the EOB effectively halted bacterial growth, as indicated by flat growth curves. The increase in the lag phase and the decrease in the growth rate at a sub-MIC concentration (12.5%) suggest a significant effect on bacterial adaptation and survival. Relative fitness analyses further highlighted the inhibitory effects of higher essential oil concentrations. S. epidermidis and E. coli had a significant (p < 0.05) reduction in fitness starting from the 6.25% concentration, while the other two species experienced a significant (p < 0.001) reduction in relative fitness from a concentration of 12.5%. These findings underscore the potential of this EOB as an effective antimicrobial agent, particularly in the context of rising antibiotic resistance. Furthermore, the study suggests that the EOB used in the present study could be integrated into therapeutic strategies as a natural alternative or adjunct to traditional antibiotics, offering a promising avenue for combating resistant bacterial strains.
Keywords: MIC; antimicrobial activity; bacterial growth; fitness cost; growth kinetics; pathogens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

