An Analysis of the Genetic Diversity, Genetic Structure, and Selection Signal of Beagle Dogs Using SNP Chips
- PMID: 40282318
- PMCID: PMC12026597
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040358
An Analysis of the Genetic Diversity, Genetic Structure, and Selection Signal of Beagle Dogs Using SNP Chips
Abstract
Background: Beagle dogs are widely used in biomedical research, but their genetic diversity and population structure require further investigation. This study aimed to assess genetic diversity, population structure, and selection signals in a foundational Beagle breeding population using genome-wide SNP genotyping.
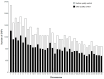
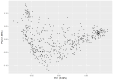
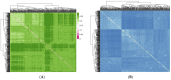
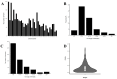
Methods: A total of 459 Beagle dogs (108 males, 351 females) were genotyped using the Canine 50K SNP chip. After quality control, 456 individuals and 31,198 SNPs were retained. Genetic diversity indices, principal component analysis (PCA), identity-by-state (IBS) distance, a genomic relationship matrix (G-matrix), runs of homozygosity (ROH), and Tajima's D selection scans were analyzed.
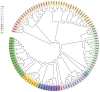
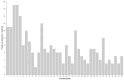
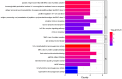
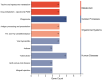
Results: The average minor allele frequency was 0.224, observed heterozygosity was 0.303, and expected heterozygosity was 0.305. A total of 2990 ROH segments were detected, with a mean inbreeding coefficient of 0.031. Phylogenetic analysis classified 106 stud dogs into 13 lineages. Selection signal analysis identified TTN (muscle function) and DLA-DRA, DLA-DOA, DLA-DMA (immune regulation) under selection.
Conclusions: The Beagle population exhibits high genetic diversity and low inbreeding. To maintain genetic stability and ensure the long-term conservation of genetic resources, structured breeding strategies should be implemented based on lineage classifications.
Keywords: SNP chips; beagle dogs; genetic diversity; genetic structure; selection signals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of genetic diversity and genetic structure of Qinchuan cattle conservation population using whole-genome resequencing.Yi Chuan. 2023 Jul 20;45(7):602-616. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.23-115. Yi Chuan. 2023. PMID: 37503584
-
Genetic Diversity of Persian Arabian Horses and Their Relationship to Other Native Iranian Horse Breeds.J Hered. 2019 Mar 5;110(2):173-182. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esy061. J Hered. 2019. PMID: 30590570
-
Comparative Analysis of Genome Diversity in Bullmastiff Dogs.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 29;11(1):e0147941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147941. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26824579 Free PMC article.
-
Measures of Homozygosity and Relationship to Genetic Diversity in the Bearded Collie Breed.Genes (Basel). 2025 Mar 27;16(4):378. doi: 10.3390/genes16040378. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40282338 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity analysis of Inner Mongolia cashmere goats (Erlangshan subtype) based on whole genome re-sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 16;25(1):698. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10485-x. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39014331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Kennel Club . The Complete Dog Book. 20th ed. Ballantine Books; New York, NY, USA: 2006.
-
- American Kennel Club Beagle Breed Standard. [(accessed on 25 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.akc.org/dog-breeds/beagle/
-
- Fédération Cynologique Internationale Beagle Breed Standard. [(accessed on 25 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.fci.be/Nomenclature/Standards/161g06-en.pdf.
-
- American Kennel Club Most Popular Dog Breeds. [(accessed on 25 December 2024)]. Available online: https://www.akc.org/most-popular-breeds/
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

