Genetic Testing in Adults over 50 Years with Chronic Kidney Disease: Diagnostic Yield and Clinical Implications in a Specialized Kidney Genetics Clinic
- PMID: 40282368
- PMCID: PMC12027001
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040408
Genetic Testing in Adults over 50 Years with Chronic Kidney Disease: Diagnostic Yield and Clinical Implications in a Specialized Kidney Genetics Clinic
Abstract
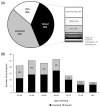
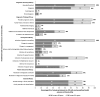
Background: Genetic causes of chronic diseases, once considered rare in adult-onset disease, now account for between 10 and 20% of cases of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Confirming a genetic diagnosis can influence disease management; however, the utility of genetic testing in older adults remains poorly understood, partly due to age-based restrictions on testing access. To better evaluate the diagnostic yield and clinical utility of genetic testing in this population, we analyzed data from adults aged ≥50 years with CKD who were assessed in a specialized kidney genetics clinic. Methods: We studied a cohort of 125 adults with CKD aged ≥50 years at the time of genetic testing. Genetic testing included gene panels targeting disease-related genes based on clinical phenotype, and/or exome sequencing for additional monogenic causes if the initial panel testing was inconclusive. Results: Pathogenic variants in disease-related genes were identified in 38% of patients. The highest diagnostic yield (48%) was in patients aged 50-54 years. The most common diagnosis post-testing was glomerulopathies (32%). Clinical utility, shown through the case series, included modifications to treatment and clinical management, as well as a reduction in the diagnostic odyssey. Conclusions: Our findings from a dedicated Kidney Genetics Clinic show that genetic testing in adults ≥50 years with CKD has significant diagnostic and clinical utility. These results support guideline recommendations that there should be no upper age limit for genetic testing. Future research in unselected CKD populations is needed to establish the broader applicability and feasibility of genetic testing in older adults.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; exome sequencing; genetic kidney disease; genetic testing; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Dahl N.K., Bloom M.S., Chebib F.T., Clark D., Westemeyer M., Jandeska S., Zhang Z., Milo-Rasouly H., Kolupaeva V., Marasa M., et al. The Clinical Utility of Genetic Testing in the Diagnosis and Management of Adults with Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023;34:2039. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000249. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Der Lee S.J., Hulsman M., Van Spaendonk R., Van Der Schaar J., Dijkstra J., Tesi N., van Ruissen F., Elting M., Reinders M., De Rojas I., et al. Prevalence of Pathogenic Variants and Eligibility Criteria for Genetic Testing in Patients Who Visit a Memory Clinic. Neurology. 2025;104:e210273. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000210273. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ganapathy A., Mishra A., Soni M.R., Kumar P., Sadagopan M., Kanthi A.V., Patric I.R.P., George S., Sridharan A., Thyagarajan T.C., et al. Multi-gene testing in neurological disorders showed an improved diagnostic yield: Data from over 1000 Indian patients. J. Neurol. 2019;266:1919–1926. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09358-1. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

