circ2LO: Identification of CircRNA Based on the LucaOne Large Model
- PMID: 40282373
- PMCID: PMC12026638
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040413
circ2LO: Identification of CircRNA Based on the LucaOne Large Model
Abstract
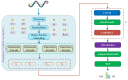
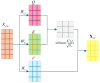
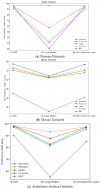
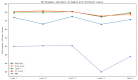
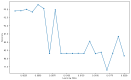
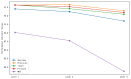
Circular RNA is a type of noncoding RNA with a special covalent bond structure. As an endogenous RNA in animals and plants, it is formed through RNA splicing. The 5' and 3' ends of the exons form circular RNA at the back-splicing sites. Circular RNA plays an important regulatory role in diseases by interacting with the associated miRNAs. Accurate identification of circular RNA can enrich the data on circular RNA and provide new ideas for drug development. At present, mainstream circular RNA recognition algorithms are divided into two categories: those based on RNA sequence position information and those based on RNA sequence biometric information. Herein, we propose a method for the recognition of circular RNA, called circ2LO, which utilizes the LucaOne large model for feature embedding of the splicing sites of RNA sequences as well as their upstream and downstream sequences to prevent semantic information loss caused by the traditional one-hot encoding method. Subsequently, it employs a convolutional layer to extract features and a self-attention mechanism to extract interactive features to accurately capture the core features of the circular RNA at the splicing sites. Finally, it uses a fully connected layer to identify circular RNA. The accuracy of circ2LO on the human dataset reached 95.47%, which is higher than the values shown by existing methods. It also achieved accuracies of 97.04% and 72.04% on the Arabidopsis and mouse datasets, respectively, demonstrating good robustness. Through rigorous validation, the circ2LO model has proven its high-precision identification capability for circular RNAs, marking it as a potentially transformative analytical platform in the circRNA research field.
Keywords: circRNA; deep learning; large language model; self-attention mechanism; transformer.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Belter A., Popenda M., Sajek M., Woźniak T., Naskręt-Barciszewska M.Z., Szachniuk M., Jurga S., Barciszewski J. A new molecular mechanism of RNA circularization and the microRNA sponge formation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022;40:3038–3045. - PubMed
-
- He Y., Fang P., Shan Y., Pan Y., Wei Y., Chen Y., Chen Y., Liu Y., Zeng Z., Zhou Z., et al. LucaOne: Generalized biological foundation model with unified nucleic acid and protein language. bioRxiv. 2024 doi: 10.1101/2024.05.10.592927. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

