The microRNA Pathway of Macroalgae: Its Similarities and Differences to the Plant and Animal microRNA Pathways
- PMID: 40282402
- PMCID: PMC12026948
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040442
The microRNA Pathway of Macroalgae: Its Similarities and Differences to the Plant and Animal microRNA Pathways
Abstract
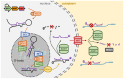
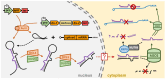
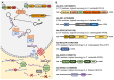
In plants and animals, the microRNA (miRNA) class of small regulatory RNA plays an essential role in controlling gene expression in all aspects of development, to respond to environmental stress, or to defend against pathogen attack. This well-established master regulatory role for miRNAs has led to each protein-mediated step of both the plant and animal miRNA pathways being thoroughly characterized. Furthermore, this degree of characterization has led to the development of a suite of miRNA-based technologies for gene expression manipulation for fundamental research or for use in industrial or medical applications. In direct contrast, molecular research on the miRNA pathway of macroalgae, specifically seaweeds (marine macroalgae), remains in its infancy. However, the molecular research conducted to date on the seaweed miRNA pathway has shown that it shares functional features specific to either the plant or animal miRNA pathway. In addition, of the small number of seaweed species where miRNA data is available, little sequence conservation of individual miRNAs exists. These preliminary findings show the pressing need for substantive research into the seaweed miRNA pathway to advance our current understanding of this essential gene expression regulatory process. Such research will also generate the knowledge required to develop novel miRNA-based technologies for use in seaweeds. In this review, we compare and contrast the seaweed miRNA pathway to those well-characterized pathways of plants and animals and outline the low degree of miRNA sequence conservation across the polyphyletic group known as the seaweeds.
Keywords: animal miRNA pathway; miRNA conservation; miRNA evolution; miRNA pathway; microRNA (miRNA); plant miRNA pathway; seaweed miRNA pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Boutet S., Vazquez F., Liu J., Béclin C., Fagard M., Gratias A., Morel J.B., Crété P., Chen X., Vaucheret H. Arabidopsis HEN1: A genetic link between endogenous miRNA controlling development and siRNA controlling transgene silencing and virus resistance. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:843–848. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00293-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

