Role of MicroRNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 40282406
- PMCID: PMC12026923
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040446
Role of MicroRNAs in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
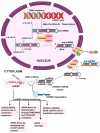
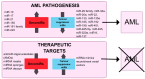
MicroRNA (miRNA), a significant class of regulatory non-coding RNA (ncRNA), can regulate the expression of numerous protein-coding messenger RNAs (mRNAs). miRNA plays an important part in shaping the human transcriptome. So far, in the human genome, about 2500 miRNAs have been found. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) belongs to a malignant clonal disorder of hematopoietic stem cells and is characterized by the uncontrolled clonal proliferation of abnormal progenitor cells in the bone marrow and blood. For the past several years, significant scientific attention has been attracted to the role of miRNAs in AML, since alterations in the expression levels of miRNAs may contribute to AML development. This review describes the main functions of non-coding RNA classes and presents miRNA biogenesis. This study aims to review recent reports about altered microRNA expression and their influence on AML cell survival, cell cycle, and apoptotic potential. Additionally, it summarizes the correlations between miRNAs and their target mRNAs in AML and outlines the role of particular miRNAs in AML subtypes according to ELN recommendations.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; microRNA; non-coding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

