Novel Truncating Variants in PODXL Represent a New Entity to Be Explored Among Podocytopathies
- PMID: 40282423
- PMCID: PMC12026838
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040464
Novel Truncating Variants in PODXL Represent a New Entity to Be Explored Among Podocytopathies
Abstract
Background/objectives: Podocalyxin is a sialoprotein mainly expressed in the kidney cortex and lung tissue, which has been described as a component of the podocyte glycocalyx. This protein promotes the reorganization of the podocyte cytoskeleton, as well as the morphogenesis and differentiation of nascent podocytes, actively participating in glomerular filtration. Previous research has suggested that PODXL haploinsufficiency leads to podocytopathy with development of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, a disorder that has been demonstrated in Podxl-deficient animal models and proposed as a primary cause in human families affected by this condition. However, only a few families have been reported, which limits the understanding about the spectrum of phenotype and prognosis of the disease.
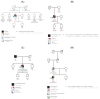
Methods: We performed high-throughput sequencing in a cohort of young adults with CKD, describing the clinical scenario of those who harbored truncating variants in the PODXL gene and testing the families for detected variants.
Results: The PODXL gene exhibited a slight deviation in loss intolerance probability and moderate deviation in the observed/expected ratio of variation, which is typically observed in dominant genes with age-dependent incomplete penetrance or variable expression. We reported four novel truncating variants in the PODXL gene, along with a collection of previously published monoallelic truncating variants.
Conclusions: These findings further support evidence about genetic defects in the PODXL gene associated with a new molecular entity of podocytopathy with adult onset. Additionally, the nucleotide sequence of PODXL contains particularities that require careful analysis to interpret the effect of the variants detected in this gene.
Keywords: CKD 1; PODXL 2; podocytopathy 3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kershaw D.B., Beck S.G., Wharram B.L., Wiggins J.E., Goyal M., Thomas P.E., Wiggins R.C. Molecular cloning and characterization of human podocalyxin-like protein. Orthologous relationship to rabbit PCLP1 and rat podocalyxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:15708–15714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.25.15708. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

