Barth Syndrome: TAFAZZIN Gene, Cardiologic Aspects, and Mitochondrial Studies-A Comprehensive Narrative Review
- PMID: 40282425
- PMCID: PMC12027479
- DOI: 10.3390/genes16040465
Barth Syndrome: TAFAZZIN Gene, Cardiologic Aspects, and Mitochondrial Studies-A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Abstract
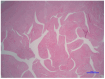
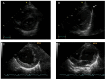
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is inherited through an X-linked pattern. The gene is located on Xq28. Male individuals who inherit the TAFAZZIN pathogenic variant will have the associated condition, while female individuals who inherit the TAFAZZIN pathogenic variant generally do not experience the condition. There are several organs that may be affected, but striking is the cardiological involvement. Cardiovascular disease, which may be the trigger starting the diagnostic procedure in a proband, may include a range of diseases from a severely dilated heart to a hypertrophic heart in the spectrum of anomalies encountered. Left ventricular non-compaction of the heart is also occasionally encountered. This cardiac event may reveal the prognosis of the affected patients. In this narrative review, we highlight the gene's characteristics, the reactome, the cardiological features of the cardiovascular disease observed in patients affected with BTHS, emphasize the most current studies on BTHS cardiomyopathy, and delineate the biological underlying mechanisms supporting the proposal of new therapeutic options.
Keywords: BTHS; Barth syndrome; TAFAZZIN; TAZ; cardiac surgery; cardiovascular disease; left ventricular non-compaction; metabolic disease; outcome; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrafamilial variability for novel TAZ gene mutation: Barth syndrome with dilated cardiomyopathy and heart failure in an infant and left ventricular noncompaction in his great-uncle.Mol Genet Metab. 2012 Nov;107(3):428-32. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.09.013. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Mol Genet Metab. 2012. PMID: 23031367 Free PMC article.
-
A Barth Syndrome Patient-Derived D75H Point Mutation in TAFAZZIN Drives Progressive Cardiomyopathy in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8201. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158201. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125771 Free PMC article.
-
Barth syndrome.Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013 Aug;163C(3):198-205. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31372. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2013. PMID: 23843353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-chain fatty acid oxidation and respiratory complex I deficiencies distinguish Barth Syndrome from idiopathic pediatric cardiomyopathy.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022 Jan;45(1):111-124. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12459. Epub 2021 Dec 7. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2022. PMID: 34821394
-
Barth Syndrome Cardiomyopathy: An Update.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 8;13(4):656. doi: 10.3390/genes13040656. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456462 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

