Maximum Entropy Production Principle of Thermodynamics for the Birth and Evolution of Life
- PMID: 40282684
- PMCID: PMC12025891
- DOI: 10.3390/e27040449
Maximum Entropy Production Principle of Thermodynamics for the Birth and Evolution of Life
Abstract
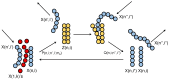
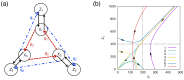
Research on the birth and evolution of life are reviewed with reference to the maximum entropy production principle (MEPP). It has been shown that this principle is essential for consistent understanding of the birth and evolution of life. First, a recent work for the birth of a self-replicative system as pre-RNA life is reviewed in relation to the MEPP. A critical condition of polymer concentration in a local system is reported by a dynamical system approach, above which, an exponential increase of entropy production is guaranteed. Secondly, research works of early stage of evolutions are reviewed; experimental research for the numbers of cells necessary for forming a multi-cellular organization, and numerical research of differentiation of a model system and its relation with MEPP. It is suggested by this review article that the late stage of evolution is characterized by formation of society and external entropy production. A hypothesis on the general route of evolution is discussed from the birth to the present life which follows the MEPP. Some examples of life which happened to face poor thermodynamic condition are presented with thermodynamic discussion. It is observed through this review that MEPP is consistently useful for thermodynamic understanding of birth and evolution of life, subject to a thermodynamic condition far from equilibrium.
Keywords: birth and evolution of life; maximum entropy production principle; multi-cellular life; non-equilibrium thermodynamics; self-replication.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Yasukazu Daigaku are employed by Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
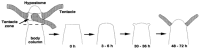
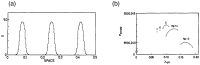
References
-
- Schrödinger E. What Is Life—The Physical Aspect of the Living Cell. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1944.
-
- Boltzmann L. Über die Beziehung zwischen dem zweiten Hauptsatze der mechanischen Wärmetheorie und der Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung respektive den Sätzen über das Wärmegleichgewicht. Wien. Ber. 1877;76:373–435.
-
- Onsager L. Reciprocal relations in irreversible processes. I. Phys. Rev. 1931;37:405–426. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.37.405. - DOI
-
- Onsager L. Reciprocal relations in irreversible processes. II. Phys. Rev. 1931;38:2265–2279. doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.38.2265. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

