Improvement of Physiological Metabolism and Flavor Quality of Eriocheir sinensis Ovaries by Dietary Supplementation with Antarctic Krill Meal
- PMID: 40282689
- PMCID: PMC12027041
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14081287
Improvement of Physiological Metabolism and Flavor Quality of Eriocheir sinensis Ovaries by Dietary Supplementation with Antarctic Krill Meal
Abstract
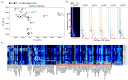
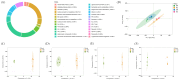
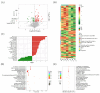
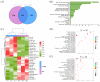
This study investigated the effects of dietary Antarctic krill meal (AKM) on the physiological metabolism and flavor quality of adult Eriocheir sinensis ovaries during the postharvest temporary rearing. The AKM concentrations tested were 0% (including negative control group and positive control group), 2%, 4%, 6%, and 8%. The results indicate that the E. sinensis ovaries in 8% AKM group produced the highest levels of aroma compounds after thermal processing, including hexanal, heptanal, phenylacetaldehyde, 3-octanone, and 2-methylbutanoic acid ethyl ester. The 8% AKM and negative control group were analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS combined with the nontargeted and widely targeted metabolomics technique. The AKM altered the composition of aroma precursors by adjusting the metabolism of glycerophospholipid, linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid, and amino acid in ovaries. Moreover, lipids composed of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) were significantly upregulated (p < 0.05). Dietary supplementation with 8% AKM had the best effect on improving the ovarian flavor quality of E. sinensis. During the postharvest temporary rearing, more aromatic precursors were produced by regulating physiological metabolism. The ovarian flavor was enhanced by lipid oxidation, Maillard reaction, and Strecker degradation during thermal processing.
Keywords: Antarctic krill meal; Eriocheir sinensis; flavor quality; metabolomics; physiological metabolism; thermal reaction pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang L., Zhang R., Jiang X., Wu X., Wang X. Dietary supplementation with synthetic astaxanthin and DHA interactively regulates physiological metabolism to improve the color and odor quality of ovaries in adult female Eriocheir sinensis. Food Chem. 2024;430:137020. - PubMed
-
- Pan J., Wu X.G., Zhao H.L., He J., Jiang X.D., Wang Y.P., Cheng Y.X. Effects of three feeding modes on the culture performance of adult pond-reared Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis) during the second year culture. Freshw. Fish. 2016;46:87–93.
-
- Tang S., Wang J.J., Li Y., Malakar P.K., Zhao Y. Recent advances in the use of antarctic krill (Euphausia superba) as a sustainable source of high-quality protein: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024;152:104684.
-
- Kaur K., Kortner T.M., Benitez-Santana T., Burri L. Effects of Antarctic krill products on feed intake, growth performance, fillet quality, and health in salmonids. Aquac. Nutr. 2022;2022:3170854.
-
- Sun P., Zhang X., Ren X., Cao Z., Zhao Y., Man H., Li D. Effect of basic amino acid pretreatment on the quality of canned Antarctic krill. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022;16:1690–1702.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

