Prediction of the Ecological Behavior of Burkholderia gladiolus in Fresh Wet Rice Noodles at Different Temperatures and Its Correlation with Quality Changes
- PMID: 40282693
- PMCID: PMC12025983
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14081291
Prediction of the Ecological Behavior of Burkholderia gladiolus in Fresh Wet Rice Noodles at Different Temperatures and Its Correlation with Quality Changes
Abstract
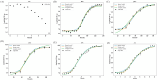
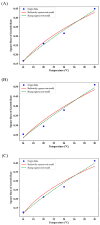
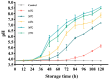
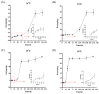
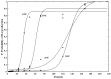
Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans (BGC) is a highly lethal foodborne pathogen responsible for outbreaks of food poisoning with the highest recorded mortality rates among bacterial foodborne illnesses in China. In this study, the ecological behavior of BGC and its Bongkrekic Acid (BA) production dynamics in fresh wet rice noodles (FWRN) were investigated under isothermal conditions ranging from 4 °C to 37 °C. Growth kinetics were modeled using the Huang, Baranyi, and modified Gompertz primary models, with secondary models (Huang square root model and Ratkowsky square root model) describing the influence of temperature on growth parameters. Among these, the Huang-Huang model combination exhibited the best performance, with a root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.009 and bias factor (Bf) and accuracy factor (Af) values close to 1. Additionally, we examined the impact of BGC contamination on the quality attributes of FWRN, including pH, color (L*, a*, b*), hardness, and moisture content. The results indicated that BGC growth significantly increased pH and yellowing (b*) values, while changes in texture and moisture were less pronounced. A probabilistic model was further developed to predict BA production under various temperature scenarios, revealing that BA formation was most likely to occur between 24 °C and 30 °C. While this study provides valuable predictive tools for microbial risk assessment and quality control of FWRN, limitations include the exclusion of additional environmental factors such as oxygen and relative humidity, as well as the lack of direct investigation into the degradation behavior of BA. Future research will expand model parameters and include sensory evaluations and advanced microbiological analyses to enhance applicability under real-world storage and transportation conditions.
Keywords: Bongkrekic Acid; food safety; growth dynamics; probabilistic model; rice and flour products.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the characteristics of Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans: Growth, bongkrekic acid production, and potential risks of food contamination in wet rice noodles and vermicelli.Food Microbiol. 2024 Jun;120:104449. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2023.104449. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Food Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38431336
-
The effect of rice and edible starch compound ratios, starch type, and rice nutrients on Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans growth and bongkrekic acid production in wet rice noodles and starch products.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2025 Jan 6;78(1):ovae124. doi: 10.1093/lambio/ovae124. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39797707
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of the Foodborne Pathogen Burkholderia gladioli pv. cocovenenans Harboring a Bongkrekic Acid Biosynthesis Gene Cluster.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 17;12:628538. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.628538. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34079526 Free PMC article.
-
Bongkrekic Acid and Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans: Formidable Foe and Ascending Threat to Food Safety.Foods. 2023 Oct 26;12(21):3926. doi: 10.3390/foods12213926. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37959045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bongkrekic Acid-a Review of a Lesser-Known Mitochondrial Toxin.J Med Toxicol. 2017 Jun;13(2):173-179. doi: 10.1007/s13181-016-0577-1. Epub 2017 Jan 19. J Med Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28105575 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kasunmala I.G.G., Navaratne S.B., Wickramasinghe I. Effect of Process Modifications and Binding Materials on Textural Properties of Rice Noodles. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020;21:100217. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2020.100217. - DOI
-
- Yi C., Zhu H., Bao J., Quan K., Yang R. The Texture of Fresh Rice Noodles as Affected by the Physicochemical Properties and Starch Fine Structure of Aged Paddy. LWT. 2020;130:109610. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109610. - DOI
-
- Jiao Z., Kawamura Y., Mishima N., Yang R., Li N., Liu X., Ezaki T. Need to Differentiate Lethal Toxin—Producing Strains of Burkholderia gladioli, Which Cause Severe Food Poisoning: Description of B. Gladioli Pathovar Cocovenenans and an Emended Description of B. gladioli. Microbiol. Immunol. 2003;47:915–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2003.tb03465.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

