Effect of Hawthorn Powder on Physical, Functional, and Sensory Characteristics of Set-Type Yogurt
- PMID: 40282778
- PMCID: PMC12026651
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14081377
Effect of Hawthorn Powder on Physical, Functional, and Sensory Characteristics of Set-Type Yogurt
Abstract
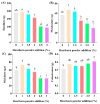
Plant powders have exhibited great potential to enhance the antioxidant activity of yogurt. This study aims to evaluate the effects of hawthorn powder (1.0-3.0%, w/w) addition on the antioxidant activity and physical properties of set-type yogurt. The results demonstrated that yogurt containing 1-2% hawthorn powder exhibited improvements in quality, water-holding capacity, and texture. Notably, the antioxidant activities, including the DPPH radical, hydroxyl radical scavenging rate, and Fe2+ chelating activity, reached 68.2 ± 4.9%, 81.6 ± 0.5%, and 72.2 ± 2.0%, respectively, and were higher than those of ordinary yogurt. Microstructural observation revealed that appropriate hawthorn powder concentration promoted homogeneous protein network formation, contributing to improved texture stability. In conclusion, this research is of interest to the development of functional dairy products.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; hawthorn powder; quality; yogurt.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Sabeena Farvin K.H., Baron C.P., Nielsen N.S., Jacobsen C. Antioxidant activity of yoghurt peptides: Part 1-in vitro assays and evaluation in ω-3 enriched milk. Food Chem. 2010;123:1081–1089. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.05.067. - DOI
-
- Pourrajab B., Fatahi S., Dehnad A., Kord Varkaneh H., Shidfar F. The impact of probiotic yogurt consumption on lipid profiles in subjects with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD. 2020;30:11–22. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2019.10.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

